Periodontal dysbiosis associates with reduced CSF Aβ42 in cognitively normal elderly
- PMID: 33869725
- PMCID: PMC8040436
- DOI: 10.1002/dad2.12172
Periodontal dysbiosis associates with reduced CSF Aβ42 in cognitively normal elderly
Abstract
Introduction: Periodontal disease is a chronic, inflammatory bacterial dysbiosis that is associated with both Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Down syndrome.
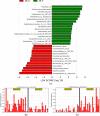
Methods: A total of 48 elderly cognitively normal subjects were evaluated for differences in subgingival periodontal bacteria (assayed by 16S rRNA sequencing) between cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarker groups of amyloid and neurofibrillary pathology. A dysbiotic index (DI) was defined at the genus level as the abundance ratio of known periodontal bacteria to healthy bacteria. Analysis of variance/analysis of covariance (ANOVA/ANCOVA), linear discriminant effect-size analyses (LEfSe) were used to determine the bacterial genera and species differences between the CSF biomarker groups.
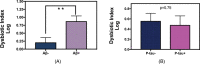
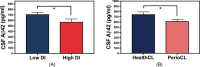
Results: At genera and species levels, higher subgingival periodontal dysbiosis was associated with reduced CSF amyloid beta (Aβ)42 (P = 0.02 and 0.01) but not with P-tau.
Discussion: We show a selective relationship between periodontal disease bacterial dysbiosis and CSF biomarkers of amyloidosis, but not for tau. Further modeling is needed to establish the direct link between oral bacteria and Aβ.
Keywords: 16S rRNA sequencing; Alzheimer's disease; CSF biomarkers; P‐tau; amyloid; infection; normal aging; oral bacterial dysbiosis; periodontitis.
© 2021 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Kaj Blennow has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, Biogen, JOMDD/Shimadzu. Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. Henrik Zetterberg has served at scientific advisory boards for Denali, Roche Diagnostics, Wave, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Pinteon Therapeutics and CogRx, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Fujirebio, Alzecure and Biogen, and is a co‐founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). No conflict of interest is reported for any of the other authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Periodontal Inflammation and Dysbiosis Relate to Microbial Changes in the Gut.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 18;12(6):1225. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061225. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930608 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Predictive Relationships between Amyloid and Tau Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease Progression: An Empirical Model.J Neurosci. 2019 Sep 11;39(37):7428-7437. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1056-19.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31350262 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's cerebrospinal biomarkers from Lumipulse fully automated immunoassay: concordance with amyloid-beta PET and manual immunoassay in Koreans : CSF AD biomarkers measured by Lumipulse in Koreans.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021 Jan 12;13(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00767-3. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33436035 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid biomarker-based molecular phenotyping of Alzheimer's disease patients in research and clinical settings.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2019;168:3-23. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 31699324 Review.
-
Polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis: An overview.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018 Mar-Apr;22(2):101-106. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_385_17. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018. PMID: 29769762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High resolution 16S rRNA gene Next Generation Sequencing study of brain areas associated with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Dec 9;14:1026260. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1026260. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36570533 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of oral microbiota are associated with the development and severity of acute pancreatitis.J Oral Microbiol. 2023 Oct 5;15(1):2264619. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2023.2264619. eCollection 2023. J Oral Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37808891 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontal Inflammation and Dysbiosis Relate to Microbial Changes in the Gut.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 18;12(6):1225. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061225. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930608 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations and correlations in dental plaque microbial communities and metabolome characteristics in patients with caries, periodontitis, and comorbid diseases.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jan 25;24(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03785-3. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38273329 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation: A Distal Consequence of Periodontitis.J Dent Res. 2022 Nov;101(12):1441-1449. doi: 10.1177/00220345221102084. Epub 2022 Jun 16. J Dent Res. 2022. PMID: 35708472 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bell JS, Spencer JI, Yates RL, Yee SA, Jacobs BM, DeLuca GC. Invited review: from nose to gut ‐ the role of the microbiome in neurological disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019;. 45(3):195‐215. - PubMed
-
- Kamer AR, Craig RG, Niederman R, Fortea J, de Leon MJ. Periodontal disease as a possible cause for Alzheimer's disease. Periodontol 2000. 2020;83:242‐271. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
