GM1 Gangliosidosis: Mechanisms and Management
- PMID: 33859490
- PMCID: PMC8044076
- DOI: 10.2147/TACG.S206076
GM1 Gangliosidosis: Mechanisms and Management
Abstract
The lysosomal storage disorder, GM1 gangliosidosis (GM1), is a neurodegenerative condition resulting from deficiency of the enzyme β-galactosidase (β-gal). Mutation of the GLB1 gene, which codes for β-gal, prevents cleavage of the terminal β-1,4-linked galactose residue from GM1 ganglioside. Subsequent accumulation of GM1 ganglioside and other substrates in the lysosome impairs cell physiology and precipitates dysfunction of the nervous system. Beyond palliative and supportive care, no FDA-approved treatments exist for GM1 patients. Researchers are critically evaluating the efficacy of substrate reduction therapy, pharmacological chaperones, enzyme replacement therapy, stem cell transplantation, and gene therapy for GM1. A Phase I/II clinical trial for GM1 children is ongoing to evaluate the safety and efficacy of adeno-associated virus-mediated GLB1 delivery by intravenous injection, providing patients and families with hope for the future.
Keywords: GLB1; GM1 gangliosidosis; LSD; biomarkers; chaperone; gene therapy.
© 2021 Rha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Douglas R Martin reports grants from National Institutes of Health, during the conduct of the study; stock options from Lysogene, and personal fees from Axovant, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
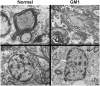
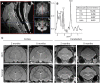
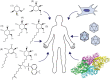
Similar articles
-
Human GLB1 knockout cerebral organoids: A model system for testing AAV9-mediated GLB1 gene therapy for reducing GM1 ganglioside storage in GM1 gangliosidosis.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019 Sep 11;21:100513. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2019.100513. eCollection 2019 Dec. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31534909 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme replacement for GM1-gangliosidosis: Uptake, lysosomal activation, and cellular disease correction using a novel β-galactosidase:RTB lectin fusion.Mol Genet Metab. 2016 Feb;117(2):199-209. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2015.12.002. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Mol Genet Metab. 2016. PMID: 26766614 Free PMC article.
-
Intracerebroventricular enzyme replacement therapy with β-galactosidase reverses brain pathologies due to GM1 gangliosidosis in mice.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 25;295(39):13532-13555. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009811. Epub 2019 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31481471 Free PMC article.
-
GM1 Gangliosidosis-A Mini-Review.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 3;12:734878. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.734878. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34539759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chaperone therapy update: Fabry disease, GM1-gangliosidosis and Gaucher disease.Brain Dev. 2013 Jun;35(6):515-23. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Brain Dev. 2013. PMID: 23290321 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare Diseases in Glycosphingolipid Metabolism.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1372:189-213. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-0394-6_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35503182
-
Zebra-Sphinx: Modeling Sphingolipidoses in Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 1;24(5):4747. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054747. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current developments of gene therapy in human diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 16;5(9):e645. doi: 10.1002/mco2.645. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39156766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Mouse Systems Genetics Approach Reveals Common and Uncommon Genetic Modifiers of Hepatic Lysosomal Enzyme Activities and Glycosphingolipids.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 3;24(5):4915. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054915. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902345 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Enzyme Replacement Therapy with a Recombinant β-Galactosidase-Lectin Fusion for CNS Delivery and Treatment of GM1-Gangliosidosis.Cells. 2022 Aug 19;11(16):2579. doi: 10.3390/cells11162579. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010656 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

