Design and Characterization of Spray-Dried Proliposomes for the Pulmonary Delivery of Curcumin
- PMID: 33854314
- PMCID: PMC8039018
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S306831
Design and Characterization of Spray-Dried Proliposomes for the Pulmonary Delivery of Curcumin
Abstract
Purpose: The goal was to directly deliver curcumin, a natural polyphenolic anticancer and anti-inflammatory compound, to the lung tissues with minimal systemic exposure through the fabrication of proliposomes, overcoming its poor aqueous solubility and oral bioavailability.
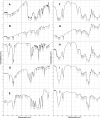
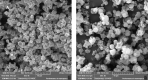
Methods: Nano-spray drying was employed to prepare proliposomes using hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin as a carrier. Lecithin and cholesterol were used as lipids, stearylamine and Poloxamer 188 were added as positive charge inducer and a surfactant, respectively. Different characterization parameters were evaluated like percentage yield, entrapment efficiency, drug loading, aerodynamic particle size, in vitro release besides morphological examination. Cytotoxicity studies on cell line A549 lung tumor cells as well as in vivo lung pharmacokinetic studies were also carried.
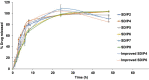
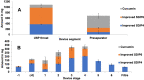
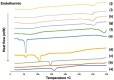
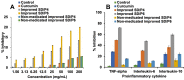
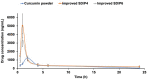
Results: The optimized formulations showed superior aerosolization properties coupled their enhanced ability to reach deep lung tissues with a high % of fine particle fraction. Cytotoxicity studies using MTT assay demonstrated enhanced growth inhibitory effect on lung tumor cells A549 and significant reduction of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 compared to the pure drug. Results of lung pharmacokinetic tests confirmed the superiority of proliposomal curcumin over curcumin powder in both, the rate and extent of lung tissue absorption, as well as the mean residence time within the lung tissues.
Conclusion: The pulmonary delivery of curcumin-loaded proliposomes as dry powder provides a direct approach to lung tissues targeting while avoiding the limitations of the oral route and offering a non-invasive alternative to the parenteral one.
Keywords: curcumin; cyclodextrin; dry powder inhalers; human epithelial cell line; proliposomes; pulmonary delivery.
© 2021 Adel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advanced spray dried proliposomes of amphotericin B lung surfactant-mimic phospholipid microparticles/nanoparticles as dry powder inhalers for targeted pulmonary drug delivery.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Oct;64:101975. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2020.101975. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33137515 Free PMC article.
-
Rifampicin-Carbohydrate Spray-Dried Nanocomposite: A Futuristic Multiparticulate Platform For Pulmonary Delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Nov 22;14:9089-9112. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S211182. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31819421 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a proliposomal pretomanid dry powder inhaler as a novel alternative approach for combating pulmonary tuberculosis.Int J Pharm. 2024 Oct 25;664:124608. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124608. Epub 2024 Aug 18. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39163929
-
A drift on liposomes to proliposomes: recent advances and promising approaches.J Liposome Res. 2022 Dec;32(4):317-331. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2021.2019762. Epub 2022 Jan 17. J Liposome Res. 2022. PMID: 35037565 Review.
-
Properties, Extraction Methods, and Delivery Systems for Curcumin as a Natural Source of Beneficial Health Effects.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Jul 3;56(7):336. doi: 10.3390/medicina56070336. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32635279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Liposomal encapsulated curcumin attenuates lung cancer proliferation, migration, and induces apoptosis.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 25;10(19):e38409. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38409. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39416833 Free PMC article.
-
A Meta-Analysis Examining the Effect of Perioperative Biologic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Medications on Postoperative Wound Complications in Various Orthopedic Surgeries.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 18;13(18):5531. doi: 10.3390/jcm13185531. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39337018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and evaluation of proliposomes formulation for enhancing the oral bioavailability of ginsenosides.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Jul;48(4):417-424. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.03.004. Epub 2024 Mar 21. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 39036737 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocarrier-Mediated Drug Delivery via Inhalational Route for Lung Cancer Therapy: A Systematic and Updated Review.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Feb 29;25(3):47. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02758-1. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38424367 Review.
-
Natural Products-Based Inhaled Formulations for Treating Pulmonary Diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Feb 23;19:1723-1748. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S451206. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38414528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

