Expression levels of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 in renal cell carcinoma and their association with lymph node metastasis
- PMID: 33850526
- PMCID: PMC8027741
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9986
Expression levels of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 in renal cell carcinoma and their association with lymph node metastasis
Abstract
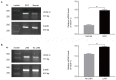
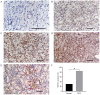
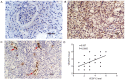
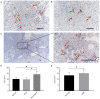
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common form of kidney cancer. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) and its receptor, VEGFR-3, are involved in lymphangiogenesis. The aim of the present study was to investigate the expression levels of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 in RCC, and their association with lymphatic vessel density (LVD) and lymph node metastasis. The mRNA expression levels of VEGF-C in 40 RCC tissues and 10 normal renal tissues were determined by reverse transcription-semiquantitative PCR. The differential expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 was examined by immunohistochemistry. Using an anti-D2-40 antibody as a lymphatic marker, the morphology and structure of lymphatic vessels in tissues was examined, and the LVD was calculated. VEGF-C mRNA expression in RCC tissues was higher than that in normal renal tissues, and VEGF-C mRNA expression in the lymph node metastasis group was higher than that in the non-lymph node metastasis group. The positive expression rate of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 in RCC tissues was significantly higher than that in normal renal tissues. VEGF-C expression in the lymph node metastasis group was significantly higher than that in the non-lymph node metastasis group, and the positive expression of VEGF-C was associated with the clinical staging of RCC. In addition, there was a correlation between VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 expression in tumor cells. The LVD around the tumor was higher than that in the center of the tumor tissues and normal renal tissues, and it was closely associated with lymphatic invasion and lymph node metastasis. Overall, the current findings demonstrated that the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signaling pathway promoted lymphangiogenesis around the tumor and provided an approach for tumor lymphatic invasion and lymph node metastasis. Therefore, VEGFC and VEGFR-3 expression may serve an important role in the initiation and development of RCC.
Keywords: lymph node metastasis; lymphatic vessel density; renal cell carcinoma; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3; vascular endothelial growth factor-C.
Copyright: © Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017 Mar-Apr;26(2):245-249. doi: 10.17219/acem/58784. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 28791841
-
Expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D as significant markers for assessment of lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010 May;293(5):802-12. doi: 10.1002/ar.21096. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010. PMID: 20225197
-
Twist modulates lymphangiogenesis and correlates with lymph node metastasis in supraglottic carcinoma.Chin Med J (Engl). 2011 May;124(10):1483-7. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011. PMID: 21740802
-
Lymphangiogenic growth factors, receptors and therapies.Thromb Haemost. 2003 Aug;90(2):167-84. doi: 10.1160/TH03-04-0200. Thromb Haemost. 2003. PMID: 12888864 Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C and its receptor-3 signaling in tumorigenesis.3 Biotech. 2023 Oct;13(10):326. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03719-4. Epub 2023 Sep 1. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37663750 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dauricine Inhibits Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Development by Regulating PTEN/AKT/mTOR and Ras/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 Pathways in a FLT4-dependent Manner.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024;24(11):1157-1168. doi: 10.2174/0115680096282997240101192452. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38321898
-
Development and validation of a machine learning model to predict the risk of lymph node metastasis in renal carcinoma.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 18;13:1054358. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1054358. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36465636 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis with the Selective VEGFR-3 Inhibitor EVT801 in Combination with Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancer Res Commun. 2022 Nov 29;2(11):1504-1519. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0151. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cancer Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36970050 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic options for different metastatic sites arising from renal cell carcinoma: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 24;103(21):e38268. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038268. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38788027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classical epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and alternative cell death process-driven blebbishield metastatic-witch (BMW) pathways to cancer metastasis.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 23;7(1):296. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01132-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35999218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
