Systematizing the genomic order and relatedness in the open reading frames (ORFs) of the coronaviruses
- PMID: 33848683
- PMCID: PMC8053407
- DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104858
Systematizing the genomic order and relatedness in the open reading frames (ORFs) of the coronaviruses
Abstract
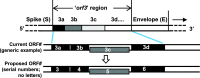
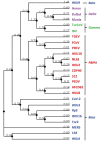
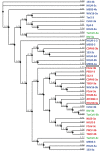
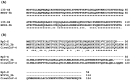
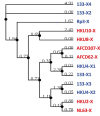
The coronaviruses (CoVs), including SARS-CoV-2, the agent of the ongoing deadly CoVID-19 pandemic (Coronavirus disease-2019), represent a highly complex and diverse class of RNA viruses with large genomes, complex gene repertoire, and intricate transcriptional and translational mechanisms. The 3'-terminal one-third of the genome encodes four structural proteins, namely spike, envelope, membrane, and nucleocapsid, interspersed with genes for accessory proteins that are largely nonstructural and called 'open reading frame' (ORF) proteins with alphanumerical designations, but not in a consistent or sequential order. Here, I report a comparative study of these ORF proteins, mainly encoded in two gene clusters, i.e. between the Spike and the Envelope genes, and between the Membrane and the Nucleocapsid genes. For brevity and focus, a greater emphasis was placed on the first cluster, collectively designated as the 'orf3 region' for ease of referral. Overall, an apparently diverse set of ORFs, such as ORF3a, ORF3b, ORF3c, ORF3d, ORF4 and ORF5, but not necessarily numbered in that order on all CoV genomes, were analyzed along with other ORFs. Unexpectedly, the gene order or naming of the ORFs were never fully conserved even within the members of one Genus. These studies also unraveled hitherto unrecognized orf genes in alternative translational frames, encoding potentially novel polypeptides as well as some that are highly similar to known ORFs. Finally, several options of an inclusive and systematic numbering are proposed not only for the orf3 region but also for the other orf genes in the viral genome in an effort to regularize the apparently confusing names and orders. Regardless of the ultimate acceptability of one system over the others, this treatise is hoped to initiate an informed discourse in this area.
Keywords: Accessory genes; Coronaviridae; Coronavirus; Open reading frame; Phylogeny; RNA genome.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Conflicting and ambiguous names of overlapping ORFs in the SARS-CoV-2 genome: A homology-based resolution.Virology. 2021 Jun;558:145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2021.02.013. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Virology. 2021. PMID: 33774510 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of accessory genes in coronavirus genomes.Virol J. 2020 Aug 27;17(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01402-1. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32854725 Free PMC article.
-
[Basic information of Coronavirus].Uirusu. 2020;70(1):29-36. doi: 10.2222/jsv.70.29. Uirusu. 2020. PMID: 33967109 Review. Japanese.
-
The coding capacity of SARS-CoV-2.Nature. 2021 Jan;589(7840):125-130. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2739-1. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Nature. 2021. PMID: 32906143
-
Corona virus versus existence of human on the earth: A computational and biophysical approach.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Oct 15;161:271-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.007. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32512089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine induces robust specific and cross-reactive IgG and unequal neutralizing antibodies in naive and previously infected people.Cell Rep. 2022 Feb 1;38(5):110336. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110336. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35090596 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

