Using RELION software within the Scipion framework
- PMID: 33825701
- PMCID: PMC8025880
- DOI: 10.1107/S2059798321001856
Using RELION software within the Scipion framework
Abstract
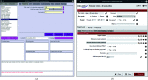
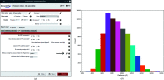
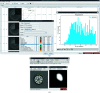
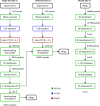
Scipion is a modular image-processing framework that integrates several software packages under a unified interface while taking care of file formats and conversions. Here, new developments and capabilities of the Scipion plugin for the widely used RELION software package are presented and illustrated with an image-processing pipeline for published data. The user interfaces of Scipion and RELION are compared and the key differences are highlighted, allowing this manuscript to be used as a guide for both new and experienced users of this software. Different on-the-fly image-processing options are also discussed, demonstrating the flexibility of the Scipion framework.
Keywords: RELION; Scipion; cryo-EM; image processing; single-particle analysis.
open access.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Robust Single-Particle Cryo-Electron Microscopy (cryo-EM) Processing Workflow with cryoSPARC, RELION, and Scipion.J Vis Exp. 2022 Jan 31;(179). doi: 10.3791/63387. J Vis Exp. 2022. PMID: 35104261
-
Using Scipion for stream image processing at Cryo-EM facilities.J Struct Biol. 2018 Dec;204(3):457-463. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 5. J Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 30296492 Free PMC article.
-
A pipeline approach to single-particle processing in RELION.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017 Jun 1;73(Pt 6):496-502. doi: 10.1107/S2059798316019276. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2017. PMID: 28580911 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of Structurally Heterogeneous Cryo-EM Data in RELION.Methods Enzymol. 2016;579:125-57. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.04.012. Epub 2016 May 31. Methods Enzymol. 2016. PMID: 27572726 Review.
-
Frealign: An Exploratory Tool for Single-Particle Cryo-EM.Methods Enzymol. 2016;579:191-226. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.04.013. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Methods Enzymol. 2016. PMID: 27572728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the decoy module of human glycoprotein 2 and uromodulin and its interaction with bacterial adhesin FimH.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022 Mar;29(3):190-193. doi: 10.1038/s41594-022-00729-3. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35273390 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of cryo-EM maps by simultaneous local and non-local deep learning.Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 3;14(1):3217. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39031-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37270635 Free PMC article.
-
Scipion-ED: a graphical user interface for batch processing and analysis of 3D ED/MicroED data.J Appl Crystallogr. 2022 Apr 22;55(Pt 3):638-646. doi: 10.1107/S1600576722002758. eCollection 2022 Jun 1. J Appl Crystallogr. 2022. PMID: 35719296 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular view of ER membrane remodeling by the Sec61/TRAP translocon.EMBO Rep. 2023 Dec 6;24(12):e57910. doi: 10.15252/embr.202357910. Epub 2023 Nov 20. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 37983950 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

