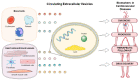
Circulating Extracellular Vesicles As Biomarkers and Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 33808038
- PMCID: PMC8001426
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11030388
Circulating Extracellular Vesicles As Biomarkers and Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are composed of a lipid bilayer containing transmembrane and soluble proteins. Subtypes of EVs include ectosomes (microparticles/microvesicles), exosomes, and apoptotic bodies that can be released by various tissues into biological fluids. EV cargo can modulate physiological and pathological processes in recipient cells through near- and long-distance intercellular communication. Recent studies have shown that origin, amount, and internal cargos (nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids) of EVs are variable under different pathological conditions, including cardiovascular diseases (CVD). The early detection and management of CVD reduce premature morbidity and mortality. Circulating EVs have attracted great interest as a potential biomarker for diagnostics and follow-up of CVD. This review highlights the role of circulating EVs as biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic follow-up of CVD, and also for drug delivery. Despite the great potential of EVs as a tool to study the pathophysiology of CVD, further studies are needed to increase the spectrum of EV-associated applications.
Keywords: RNA; biomarkers; cardiovascular disease; ectosomes; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; lipids; proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome of Extracellular Vesicles: State-of-the-Art.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 28;10:202. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00202. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30873152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Theranostics.Theranostics. 2017 Sep 26;7(17):4168-4182. doi: 10.7150/thno.21274. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 29158817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle interplay in cardiovascular pathophysiology.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):H1749-H1761. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00925.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33666501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Pathophysiology: Communications, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Potential.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Aug;24(8):711-726. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09875-0. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38844744 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular disease: Biological functions and therapeutic implications.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 May;233:108025. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.108025. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34687770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Strategy of Mesenchymal-Stem-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Regenerative Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 9;23(12):6480. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126480. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Alveolar Epithelial-Capillary Barrier Disruption in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Pathophysiological Role and Therapeutic Potential.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 23;12:752287. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.752287. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34887773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing the presence of tear extracellular vesicles in Keratoconus.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Nov;224:109242. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109242. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 36084727 Free PMC article.
-
Lim Domain Binding 3 (Ldb3) Identified as a Potential Marker of Cardiac Extracellular Vesicles.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 1;23(13):7374. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137374. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806378 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes and exosomal miRNAs: A new therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 8;13:992476. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.992476. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Théry C., Witwer K.W., Aikawa E., Alcaraz M.J., Anderson J.D., Andriantsitohaina R., Antoniou A., Arab T., Archer F., Atkin-Smith G.K., et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2018;7 doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials