Preparation of Microemulsion from an Alkyl Polyglycoside Surfactant and Tea Tree Oil
- PMID: 33807380
- PMCID: PMC8037010
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26071971
Preparation of Microemulsion from an Alkyl Polyglycoside Surfactant and Tea Tree Oil
Abstract
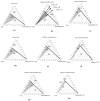
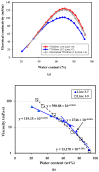
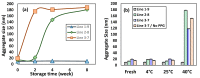
Preparation and characterization of microemulsions consisting of a plant-derived alkyl polyglycoside (APG) surfactant and the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) was studied. This nonionic APG surfactant used was Triton CG-110 with a CMC at 1748 ppm at 25 °C. Tea tree oil (TTO) was extracted from tea tree leaves by Triton CG-110-assisted hydrodistillation method. The preparation of the microemulsion was aided by the construction of pseudo-ternary phase diagrams, which were investigated at the different weight ratios of surfactant mixtures (Smix = Triton CG-110/PPG) as 0.6:1, 1.8:1, 1:0 with hydrodistilled and commercial TTO by water titration method at room temperature. Particularly, structure of microemulsion was identified by electrical conductivity and viscosity. Moreover, shelf stability of some microemulsion made of 1% TTO with various concentration of Triton CG-110/PPG (1.8:1 w/w) were monitored for over a two-month period with dynamic light scattering. These results showed that microemulsion made of 1% TTO, 9% Triton CG-110/PPG (1.8:1 w/w) was insensitive with time and temperature of storage.
Keywords: alkyl polyglycoside; humectant; hydrodistillation; microemulsion; tea tree oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crotamiton-loaded tea tree oil containing phospholipid-based microemulsion hydrogel for scabies treatment: in vitro, in vivo evaluation, and dermatokinetic studies.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):1972-1981. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1979131. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34565260 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia) oil as a natural antimicrobial agent in lipophilic formulations.Can J Microbiol. 2015 Jan;61(1):82-8. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2014-0667. Can J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25515896
-
Development, optimization, and characterization of a novel tea tree oil nanogel using response surface methodology.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016 Sep;42(9):1434-45. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2016.1141931. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26821208
-
Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil and its monoterpene constituents in treating protozoan and helminthic infections.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Oct;130:110624. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110624. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 33503761 Review.
-
Can the tea tree oil (Australian native plant: Melaleuca alternifolia Cheel) be an alternative treatment for human demodicosis on skin?Parasitology. 2018 Oct;145(12):1510-1520. doi: 10.1017/S0031182018000495. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Parasitology. 2018. PMID: 29667560 Review.
Cited by
-
Micro-nanoemulsion and nanoparticle-assisted drug delivery against drug-resistant tuberculosis: recent developments.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2023 Dec 20;36(4):e0008823. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00088-23. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 38032192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoemulsion as an Effective Inhibitor of Biofilm-forming Bacterial Associated Drug Resistance: An Insight into COVID Based Nosocomial Infections.Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2022;27(4):543-555. doi: 10.1007/s12257-022-0055-3. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2022. PMID: 36092682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advance of Microemulsion and Application for Enhanced Oil Recovery.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jun 10;14(12):1004. doi: 10.3390/nano14121004. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient Development of Green Emulsifier/Emollient-Based Emulsion Vehicles: From RSM Optimal Experimental Design to Abridged In Vivo Assessment.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 1;15(2):486. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020486. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839806 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Carboxyl Modified Polyether Polysiloxane Surfactant for the Biodegradable Foam Fire Extinguishing Agents.Molecules. 2023 Apr 18;28(8):3546. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083546. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holmberg K. Natural surfactants. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001;6:148–159. doi: 10.1016/S1359-0294(01)00074-7. - DOI
-
- Ruiz C.C. Sugar-Based Surfactants: Fundamentals and Applications. CRC Press; Waretown, NJ, USA: 2008.
-
- Wang L., Queneau Y. Carbohydrate-Based Amphiphiles: Resource for Bio-Based Surfactants. J.B. Metzler; Stuttgart, Germany: 2018. pp. 1–35.
-
- Ranieri D., Preisig N., Stubenrauch C. On the Influence of Intersurfactant H-Bonds on Foam Stability: A Study with Technical Grade Surfactants. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2018;55:6–16. doi: 10.3139/113.110537. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

