Immunologically Inert Nanostructures as Selective Therapeutic Tools in Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 33806746
- PMCID: PMC8004653
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10030707
Immunologically Inert Nanostructures as Selective Therapeutic Tools in Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
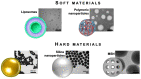
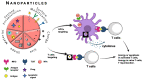
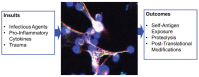
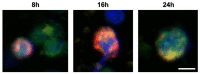
The current therapies based on immunosuppressant or new biologic drugs often show some limitations in term of efficacy and applicability, mainly because of their inadequate targeting and of unwanted adverse reactions they generate. To overcome these inherent problems, in the last decades, innovative nanocarriers have been developed to encapsulate active molecules and offer novel promising strategies to efficiently modulate the immune system. This review provides an overview of how it is possible, exploiting the favorable features of nanocarriers, especially with regard to their immunogenicity, to improve the bioavailability of novel drugs that selectively target immune cells in the context of autoimmune disorders and inflammatory diseases. A focus is made on nanoparticles that selectively target neutrophils in inflammatory pathologies.
Keywords: NETosis; drug targeting; immunomodulation; nanoparticles; neutrophils; therapeutic carriers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Silica-Based Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: From Nanocarriers to Biomodulators.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Aug 18;53(8):1545-1556. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00280. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 32667182
-
Nanomaterials for direct and indirect immunomodulation: A review of applications.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Jan 15;142:105139. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2019.105139. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 31704342 Review.
-
Nanocarriers as Tools in Delivering Active Compounds for Immune System Related Pathologies.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2016;10(2):128-45. doi: 10.2174/1872210510999160427113345. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27502390 Review.
-
Polymeric vesicles: from drug carriers to nanoreactors and artificial organelles.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Oct 18;44(10):1039-49. doi: 10.1021/ar200036k. Epub 2011 May 24. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21608994 Review.
-
Active Targeting of Drugs and Bioactive Molecules via Oral Administration by Ligand-Conjugated Lipidic Nanocarriers: Recent Advances.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018 Dec 18;20(1):15. doi: 10.1208/s12249-018-1262-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018. PMID: 30564942 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles to Target and Treat Macrophages: The Ockham's Concept?Pharmaceutics. 2021 Aug 26;13(9):1340. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091340. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Elasticity of Gelatin Nanoparticles on the Interaction with Macrophages.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 6;15(1):199. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010199. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678828 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

