Translational Approaches with Antioxidant Phytochemicals against Alcohol-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Gut Dysbiosis, Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, and Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 33806556
- PMCID: PMC8000766
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10030384
Translational Approaches with Antioxidant Phytochemicals against Alcohol-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Gut Dysbiosis, Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, and Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
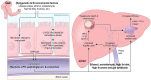
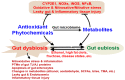
Emerging data demonstrate the important roles of altered gut microbiomes (dysbiosis) in many disease states in the peripheral tissues and the central nervous system. Gut dysbiosis with decreased ratios of Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes and other changes are reported to be caused by many disease states and various environmental factors, such as ethanol (e.g., alcohol drinking), Western-style high-fat diets, high fructose, etc. It is also caused by genetic factors, including genetic polymorphisms and epigenetic changes in different individuals. Gut dysbiosis, impaired intestinal barrier function, and elevated serum endotoxin levels can be observed in human patients and/or experimental rodent models exposed to these factors or with certain disease states. However, gut dysbiosis and leaky gut can be normalized through lifestyle alterations such as increased consumption of healthy diets with various fruits and vegetables containing many different kinds of antioxidant phytochemicals. In this review, we describe the mechanisms of gut dysbiosis, leaky gut, endotoxemia, and fatty liver disease with a specific focus on the alcohol-associated pathways. We also mention translational approaches by discussing the benefits of many antioxidant phytochemicals and/or their metabolites against alcohol-mediated oxidative stress, gut dysbiosis, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and fatty liver disease.
Keywords: antioxidant; dysbiosis; endotoxemia; ethanol; fatty liver disease; gut microbiome; inflammation; leaky gut; oxidative stress; phytochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ellagic Acid Prevents Binge Alcohol-Induced Leaky Gut and Liver Injury through Inhibiting Gut Dysbiosis and Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Aug 30;10(9):1386. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091386. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573017 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal HIF-1α deletion exacerbates alcoholic liver disease by inducing intestinal dysbiosis and barrier dysfunction.J Hepatol. 2018 Oct;69(4):886-895. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.021. Epub 2018 May 25. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29803899 Free PMC article.
-
Mulberry and dandelion water extracts prevent alcohol-induced steatosis with alleviating gut microbiome dysbiosis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Jul;243(11):882-894. doi: 10.1177/1535370218789068. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 30105955 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Gut Dysbiosis in Liver Diseases: What Have We Learned So Far?Diseases. 2019 Nov 12;7(4):58. doi: 10.3390/diseases7040058. Diseases. 2019. PMID: 31726747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota and Host Reaction in Liver Diseases.Microorganisms. 2015 Oct 28;3(4):759-91. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms3040759. Microorganisms. 2015. PMID: 27682116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic strategies of small molecules in the microbiota-gut-brain axis for alcohol use disorder.Drug Discov Today. 2023 May;28(5):103552. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103552. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 36907319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Total Gastrointestinal Flora Transplantation in the Treatment of Leaky Gut Syndrome and Flora Loss.Cureus. 2022 Nov 3;14(11):e31071. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31071. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36475195 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Gut Dysbiosis in the Pathogenesis and Management of Ischemic Stroke.Cells. 2022 Apr 6;11(7):1239. doi: 10.3390/cells11071239. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Randomized Clinical Trial: Probiotics Alleviated Oral-Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal-Related Complications in Thyroid Cancer Patients Before Radioiodine Therapy Following Thyroidectomy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 8;13:834674. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.834674. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35350100 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sex-Specific Effect of Ethanol on Colon Content Lipidome in a Mice Model Using Nontargeted LC/MS.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 29;9(14):16044-16054. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09597. eCollection 2024 Apr 9. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38617688 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

