Dysregulation of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Human Malignancies: A Window for Therapeutic Intervention
- PMID: 33805973
- PMCID: PMC8037609
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13071513
Dysregulation of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Human Malignancies: A Window for Therapeutic Intervention
Abstract
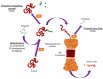
The ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) governs the non-lysosomal degradation of oxidized, damaged, or misfolded proteins in eukaryotic cells. This process is tightly regulated through the activation and transfer of polyubiquitin chains to target proteins which are then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome complex. The role of UPS is crucial in regulating protein levels through degradation to maintain fundamental cellular processes such as growth, division, signal transduction, and stress response. Dysregulation of the UPS, resulting in loss of ability to maintain protein quality through proteolysis, is closely related to the development of various malignancies and tumorigenesis. Here, we provide a comprehensive general overview on the regulation and roles of UPS and discuss functional links of dysregulated UPS in human malignancies. Inhibitors developed against components of the UPS, which include U.S. Food and Drug Administration FDA-approved and those currently undergoing clinical trials, are also presented in this review.
Keywords: cancer; chemoresistance; dysregulation; inhibitors; therapy; ubiquitin proteasome system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in kidney diseases.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012 Aug;16(4):507-17. doi: 10.1007/s10157-012-0643-1. Epub 2012 Jun 9. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22684356 Review.
-
Targeting the ubiquitin proteasome system in haematological malignancies.Blood Rev. 2013 Nov;27(6):297-304. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 19. Blood Rev. 2013. PMID: 24183816 Review.
-
Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in brain ischemia: friend or foe?Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jan;112:50-69. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24157661 Review.
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome system and its role in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.Cell Mol Immunol. 2006 Aug;3(4):255-61. Cell Mol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16978533 Review.
-
Ubiquitin Engineering for Interrogating the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and Novel Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2023 Aug 21;12(16):2117. doi: 10.3390/cells12162117. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteostasis and neurodegeneration: a closer look at autophagy in Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Nov 2;15:1281338. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1281338. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38020769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasome Inhibitors Decrease the Viability of Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells by Restoring Mitofusin-2 Expression under Hypoxic Conditions.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 9;10(4):873. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040873. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453623 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Secondary Metabolites as Inhibitors of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 10;22(24):13309. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413309. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The gold complex auranofin: new perspectives for cancer therapy.Discov Oncol. 2021 Oct 20;12(1):42. doi: 10.1007/s12672-021-00439-0. Discov Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35201489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UBE2T/STAT3 Signaling Promotes the Proliferation and Tumorigenesis in Retinoblastoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Aug 2;63(9):20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.9.20. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35980647 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

