Downregulation of Snail by DUSP1 Impairs Cell Migration and Invasion through the Inactivation of JNK and ERK and Is Useful as a Predictive Factor in the Prognosis of Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 33800291
- PMCID: PMC7962644
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13051158
Downregulation of Snail by DUSP1 Impairs Cell Migration and Invasion through the Inactivation of JNK and ERK and Is Useful as a Predictive Factor in the Prognosis of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
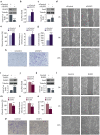
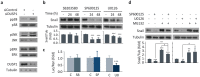
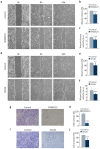
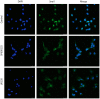
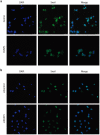
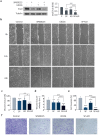
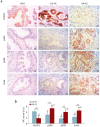
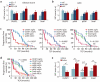
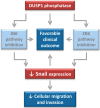
Dual specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1) is crucial in prostate cancer (PC), since its expression is downregulated in advanced carcinomas. Here, we investigated DUSP1 effects on the expression of mesenchymal marker Snail, cell migration and invasion, analyzing the underlying mechanisms mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) inhibition. To this purpose, we used different PC cells overexpressing or lacking DUSP1 or incubated with MAPKs inhibitors. Moreover, we addressed the correlation of DUSP1 expression with Snail and activated MAPKs levels in samples from patients diagnosed with benign hyperplasia or prostate carcinoma, studying its implication in tumor prognosis and survival. We found that DUSP1 downregulates Snail expression and impairs migration and invasion in PC cells. Similar results were obtained following the inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK). In clinical samples, we evidenced an inverse correlation between DUSP1 expression and Snail levels, which are further associated with JNK and ERK activation. Consequently, the pattern DUSP1high/activated JNKlow/activated ERKlow/Snaillow is associated with an overall extended survival of PC patients. In summary, the ratio between DUSP1 and Snail expression, with additional JNK and ERK activity measurement, may serve as a potential biomarker to predict the clinical outcome of PC patients. Furthermore, DUSP1 induction or inhibition of JNK and ERK pathways could be useful to treat PC.
Keywords: DUSP1; MAPK; Snail; biomarkers; migration and invasion; patient survival; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase D activity is a risk biomarker in prostate cancer that drives cell invasion by a Snail/ERK dependent mechanism.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024 Jan;1870(1):166851. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166851. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024. PMID: 37611675
-
USP49 inhibits ischemia-reperfusion-induced cell viability suppression and apoptosis in human AC16 cardiomyocytes through DUSP1-JNK1/2 signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):6529-6538. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27390. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30246457
-
Dual-specificity phosphatase 1 ubiquitination in extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated control of growth in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2008 Jun 1;68(11):4192-200. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6157. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18519678
-
Role of Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 1 in Glucocorticoid-Driven Anti-inflammatory Responses.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01446. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31316508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of DUSP1/MKP1 in tumorigenesis, tumor progression and therapy.Cancer Med. 2016 Aug;5(8):2061-8. doi: 10.1002/cam4.772. Epub 2016 May 26. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27227569 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early growth response 1 regulates dual‑specificity protein phosphatase 1 and inhibits cell migration and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2024 Apr 3;27(6):240. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14373. eCollection 2024 Jun. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38623570 Free PMC article.
-
piRNA PROPER Suppresses DUSP1 Translation by Targeting N6-Methyladenosine-Mediated RNA Circularization to Promote Oncogenesis of Prostate Cancer.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(33):e2402954. doi: 10.1002/advs.202402954. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38962952 Free PMC article.
-
LPAR5 confers radioresistance to cancer cells associated with EMT activation via the ERK/Snail pathway.J Transl Med. 2022 Oct 5;20(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03673-4. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36199069 Free PMC article.
-
hnRNPA2B1 Promotes Colon Cancer Progression via the MAPK Pathway.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 22;12:666451. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.666451. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34630502 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of parathyroid hormone-related peptide in the aggressive phenotype of colorectal cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Nov 7;27(41):7025-7040. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i41.7025. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34887626 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

