Japanese subpopulation analysis of MONARCH 2: phase 3 study of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant for treatment of hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer that progressed on endocrine therapy
- PMID: 33797023
- PMCID: PMC8354907
- DOI: 10.1007/s12282-021-01239-8
Japanese subpopulation analysis of MONARCH 2: phase 3 study of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant for treatment of hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer that progressed on endocrine therapy
Abstract
Background: This was a Japanese subpopulation analysis of MONARCH 2, a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant in patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer (ABC).
Methods: Eligible women had progressed on (neo)adjuvant endocrine therapy (ET), ≤ 12 months from end of adjuvant ET, or on first-line ET for ABC, and had not received chemotherapy for ABC. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive abemaciclib or placebo plus fulvestrant. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS). Secondary endpoints included overall survival (OS), pharmacokinetics (PK), health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and safety.
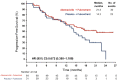
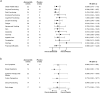
Results: In Japan, 95 patients were randomized (abemaciclib, n = 64; placebo, n = 31). At final PFS analysis (February 14, 2017), median PFS was 21.2 and 14.3 months, respectively, in the abemaciclib and placebo groups (hazard ratio: 0.672; 95% confidence interval: 0.380-1.189). Abemaciclib had a higher objective response rate (37.5%) than placebo (12.9%). PK and safety profiles for Japanese patients were consistent with those of the overall population, without clinically meaningful differences across most HRQoL dimensions evaluated. The most frequent adverse events in the abemaciclib versus placebo groups were diarrhea (95.2 versus 25.8%), neutropenia (79.4 versus 0%), and leukopenia (66.7 versus 0%). At a second data cutoff (June 20, 2019), median OS was not reached with abemaciclib and 47.3 months with placebo (hazard ratio: 0.755; 95% confidence interval: 0.390-1.463).
Conclusions: Results of the Japanese subpopulation were consistent with the improved clinical outcomes and manageable safety profile observed in the overall population.
Clinical trial registration: NCT02107703; U.S. National Library of Medicine: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02107703 .
Keywords: Abemaciclib; Breast cancer; Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Kenichi Inoue reports personal fees and grants to institution from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and Pfizer Japan; and grants to institution from AstraZeneca, Bayer, MSD, Novartis Pharma K.K., Parexel/Puma Biotechnology, and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Norikazu Masuda reports personal fees, grants, and other support (research funding to institution) from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Eisai Co., Ltd.; personal fees and other support (research funding to institution) from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Pfizer Japan, Inc., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd; and other support (research funding to institution) from MSD and Nippon-Kayaku. Hiroji Iwata reports personal fees and grants from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., and Pfizer Japan, Inc.; grants from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD, Nippon Kayaku, and Sanofi, and personal fees from Eisai Co., Ltd. Masato Takahashi reports personal fees from Astra Zeneca, Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and Pfizer Japan, Inc. Yoshinori Ito reports grants from A2 Healthcare, AstraZeneca, Covance, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., EPS International Holdings Co., Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., MSD, Novartis Pharma K.K., Parexel, QVIA Services Japan K.K., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Yasuo Miyoshi reports personal fees and grants from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., MSD, Pfizer Japan, Inc., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Takahiro Nakayama reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Novartis Pharma K.K., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Hirofumi Mukai reports personal fees and grants from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. and Pfizer Japan, Inc.; research grants from the Japanese government; personal fees from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd.; and membership on the Board of Directors of the Japan Breast Cancer Society. Antonio Llombart-Cussac reports grants, personal fees, and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; grants and non-financial support from Eisai Co., Ltd.; grants and personal fees from Genomic Health, Inc. and GSK Tesaro; personal fees and non-financial support from Bristol; personal fees from MSD; and stock, patents, and intellectual property with MedSIR. George W. Sledge, Jr. reports personal fees from Syndax and Verseau, Inc.; grants from Pfizer; and other (board of directors) from Tessa Therapeutics. Masakazu Toi reports personal fees, grants, and other role or support from Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. and Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd.; personal fees and grants from AstraZeneca, C&C Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Nippon Kayaku, Pfizer Japan, Inc., Shimadzu, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd., and Yakult; grants and other role or support from Luxonus, Inc.; personal fees and other role or support from Eli Lilly Japan K.K. and Konica Minolta, Inc.; grants from AFI Technologies, Astellas Pharma, Inc., GL Sciences, the Japanese Breast Cancer Research Group Association, and Shionogi; personal fees from Exact Science, Genomic Health, Inc., MSD, and Novartis Pharma K.K.; other role or support from Athenex Oncology, Bertis, Inc., BMS, Terumo Corporation, and Kansai Medical Net; and membership on the Board of Directors of the Japanese Breast Cancer Research Group Association, Organisation for Oncology and Translational Research, and Kyoto Breast Cancer Research Network. Joji Mori, Sachi Sakaguchi, Tsutomu Kawaguchi, and Yoshinori Tanizawa are employees and minor shareholders of Eli Lilly Japan K.K. Jan-Stefan van der Walt is an employee and minor shareholder of Eli Lilly and Company, UK.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Effect of Abemaciclib Plus Fulvestrant on Overall Survival in Hormone Receptor-Positive, ERBB2-Negative Breast Cancer That Progressed on Endocrine Therapy-MONARCH 2: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jan 1;6(1):116-124. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.4782. JAMA Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31563959 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Abemaciclib plus fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer in premenopausal women: subgroup analysis from the MONARCH 2 trial.Breast Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 23;23(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01463-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34425869 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib in Combination With Fulvestrant in Women With HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer Who Had Progressed While Receiving Endocrine Therapy.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Sep 1;35(25):2875-2884. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.7585. Epub 2017 Jun 3. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28580882 Clinical Trial.
-
[Development of CDK4 & 6 Inhibitor Abemaciclib in Breast Cancer].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2021 Dec;48(12):1475-1483. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2021. PMID: 34911915 Review. Japanese.
-
Abemaciclib: safety and effectiveness of a unique cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2020 Aug;19(8):945-954. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2020.1781814. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2020. PMID: 32552035 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Absolute Lymphocyte Count With Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Breast Cancer in the MONARCH 2 Trial.Oncologist. 2024 Mar 4;29(3):e319-e329. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad301. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 37971418 Free PMC article.
-
Safety in Japanese Advanced Breast Cancer Patients Who Received Abemaciclib in MONARCH 2 and MONARCH 3: Assessment of Treatment-Emergent Neutropenia, Diarrhea, and Increased Alanine Aminotransferase and Aspartate Aminotransferase Levels.Cancer Manag Res. 2022 Mar 19;14:1179-1194. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S348591. eCollection 2022. Cancer Manag Res. 2022. PMID: 35342308 Free PMC article.
-
Japanese subgroup analysis of the phase 3 MONARCH 3 study of abemaciclib as initial therapy for patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2022 Jan;29(1):174-184. doi: 10.1007/s12282-021-01295-0. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34661821 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Detection of high-risk patients resistant to CDK4/6 inhibitors with hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative advanced and metastatic breast cancer in Japan (KBCSG-TR-1316).Breast Cancer. 2023 Nov;30(6):943-951. doi: 10.1007/s12282-023-01485-y. Epub 2023 Jul 24. Breast Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37486454 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world incidence of and risk factors for abemaciclib-induced interstitial lung disease in Japan: a nested case-control study of abemaciclib-induced interstitial lung disease (NOSIDE).Breast Cancer. 2025 Jan;32(1):177-185. doi: 10.1007/s12282-024-01648-5. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39556171
References
-
- GLOBOCAN Breast Cancer fact sheet. In.; 2018. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/pdf/fact-sheets/cancers/cancer-fact-sheet...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

