Exosomes derived from microRNA-512-5p-transfected bone mesenchymal stem cells inhibit glioblastoma progression by targeting JAG1
- PMID: 33795521
- PMCID: PMC8064202
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202747
Exosomes derived from microRNA-512-5p-transfected bone mesenchymal stem cells inhibit glioblastoma progression by targeting JAG1
Abstract
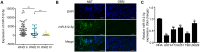
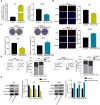
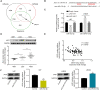
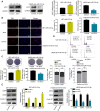
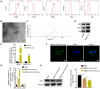
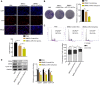
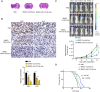
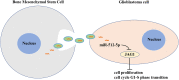
In this study, we demonstrate that bone mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC)-derived exosomes alter tumor phenotypes by delivering miR-512-5p. miR-512-5p was downregulated in glioblastoma tissues and cells, and Jagged 1 (JAG1) was the target gene of miR-512-5p. We clarified the expression patterns of miR-512-5p and JAG1 along with their interactions in glioblastoma. Additionally, we observed that BMSC-derived exosomes could contain and transport miR-512-5p to glioblastoma cells in vitro. BMSC-derived exosomal miR-512-5p inhibited glioblastoma cell proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest by suppressing JAG1 expression. In vivo assays validated the in vitro findings, with BMSC-exosomal miR-512-5p inhibiting glioblastoma growth and prolonging survival in mice. These results suggest that BMSC-derived exosomes transport miR-512-5p into glioblastoma and slow its progression by targeting JAG1. This study reveals a new molecular mechanism for glioblastoma treatment and validates miRNA packaging into exosomes for glioblastoma cell communication.
Keywords: bone mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC); exosomes; glioblastoma (GBM); jagged 1 (JAG1); miR-512-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Effects of Exosomal miRNA-4731-5p from Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells on Human Glioblastoma Cells.Arch Med Res. 2024 Nov;55(7):103061. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2024.103061. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Arch Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39098111
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-133b suppresses glioma progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting EZH2.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Dec 16;10(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1446-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31842978 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-16-5p-containing exosomes derived from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion, while promoting apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating ITGA2.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Nov;234(11):21380-21394. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28747. Epub 2019 May 17. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31102273
-
Mesenchymal stem cells in glioblastoma therapy and progression: How one cell does it all.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Aug;1876(1):188582. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188582. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34144129 Review.
-
Belonging to a network--microRNAs, extracellular vesicles, and the glioblastoma microenvironment.Neuro Oncol. 2015 May;17(5):652-62. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou292. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25301812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The potential applications of artificially modified exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in tumor therapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 4;13:1299384. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1299384. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38250549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Based Therapy for the Treatment of Glioblastoma: An Update from Preclinical to Clinical Studies.Cells. 2021 Dec 30;11(1):116. doi: 10.3390/cells11010116. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as new tools for delivery of miRNAs in the treatment of cancer.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 26;10:956563. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.956563. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36225602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-126 in Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Hepatoblastoma Cells Promotes the Tumorigenesis of Hepatoblastoma through Inducing the Differentiation of BMSCs into Cancer Stem Cells.J Immunol Res. 2021 Oct 29;2021:6744715. doi: 10.1155/2021/6744715. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34746322 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-based and cell-free immunotherapies for glioblastoma: current status and future directions.Front Immunol. 2023 May 25;14:1175118. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1175118. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37304305 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

