The m6A Reader YTHDF1 Facilitates the Tumorigenesis and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via USP14 Translation in an m6A-Dependent Manner
- PMID: 33791305
- PMCID: PMC8006284
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.647702
The m6A Reader YTHDF1 Facilitates the Tumorigenesis and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via USP14 Translation in an m6A-Dependent Manner
Abstract
Objectives: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation is implicated in the progression of multiple cancers via influencing mRNA modification. YTHDF1 can act as an oncogene in gastric cancer (GC), while the biological mechanisms via which YTHDF1 regulates gastric tumorigenesis through m6A modification remain largely unknown.
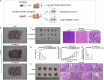
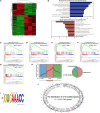
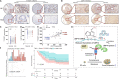
Methods: GEO and TCGA cohorts were analyzed for differentially expressed m6A modification components in GC clinical specimens and their association with clinical prognosis. Transwell and flow cytometry assays as well as subcutaneous xenograft and lung metastasis models were used to evaluate the phenotype of YTHDF1 in GC. Intersection of RNA/MeRIP-seq, luciferase assay, RIP-PCR, RNA pull-down and MeRIP-PCR was used to identify YTHDF1- modified USP14 and its m6A levels in GC cells.
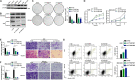
Results: High-expressed YTHDF1 was found in GC tissues and was related to poor prognosis, acting as an independent prognostic factor of poor survival in GC patients. YTHDF1 deficiency inhibited cell proliferation and invasion (in vitro), and gastric tumorigenesis and lung metastasis (in vivo) and also induced cell apoptosis. Intersection assays revealed that YTHDF1 promoted USP14 protein translation in an m6A-dependent manner. USP14 upregulation was positively correlated with YTHDF1 expression and indicated a poor prognosis in GC.
Conclusion: Our data suggested that m6A reader YTHDF1 facilitated tumorigenesis and metastasis of GC by promoting USP14 protein translation in an m6A-dependent manner and might provide a potential target for GC treatment.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; USP14; YTHDF1; gastric cancer; metastasis; tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Liang, Yi, Fan, Chen, Zhang and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
YTHDF1 Aggravates the Progression of Cervical Cancer Through m6A-Mediated Up-Regulation of RANBP2.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 19;11:650383. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.650383. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33816306 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF1 promotes breast cancer progression by facilitating FOXM1 translation in an m6A-dependent manner.Cell Biosci. 2022 Feb 23;12(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00759-w. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35197112 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF1 Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells via Upregulating TCF7 mRNA Translation.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Mar 20;29(3):117. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2903117. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38538279
-
N6-Methyladenosine RNA-Binding Protein YTHDF1 in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Function, Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Implication.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;14(14):3489. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143489. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential role of m6A reader YTHDF1 as diagnostic biomarker and the signaling pathways in tumorigenesis and metastasis in pan-cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jan 28;9(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01321-4. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36707507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Advances in the Development of Epigenetic Modifications Therapeutic Drugs Delivery Systems.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Oct 19;19:10623-10637. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S480095. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39445155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in RNA m6A Modification in Solid Tumors and Tumor Immunity.Cancer Treat Res. 2023;190:95-142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-45654-1_4. Cancer Treat Res. 2023. PMID: 38113000
-
Identification and validation of signature for prognosis and immune microenvironment in gastric cancer based on m6A demethylase ALKBH5.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 6;12:1079402. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1079402. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686788 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant RNA m6A modification in gastrointestinal malignancies: versatile regulators of cancer hallmarks and novel therapeutic opportunities.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Apr 4;14(4):236. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05736-w. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37015927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into the structure, physiological function, and role in cancer of m6A readers-YTH domain-containing proteins.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Mar 28;8(1):137. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00947-0. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35351856 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cerami E., Gao J., Dogrusoz U., Gross B. E., Sumer S. O., Aksoy B. A., et al. (2012). The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2 401–404. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

