MLKL inhibits intestinal tumorigenesis by suppressing STAT3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 33767595
- PMCID: PMC7975698
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.56152
MLKL inhibits intestinal tumorigenesis by suppressing STAT3 signaling pathway
Abstract
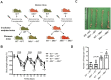
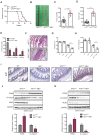
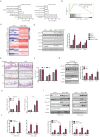
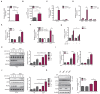
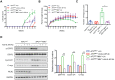
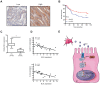
Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) plays an important role in necroptosis, but the role and mechanism of MLKL in intestinal tumorigenesis remain unclear. Here, we found that hematopoietic- and nonhematopoietic-derived MLKL affected intestinal inflammation, but nonhematopoietic-derived MLKL primarily inhibited intestinal tumorigenesis. Loss of MLKL enhanced intestinal regeneration and the susceptibility to intestinal tumorigenesis in Apcmin/+ mice by hyperactivating the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/ signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) axis. Furthermore, MLKL deficiency increased interleukin-6 (IL-6) production in dendritic cells. Administration of anti-IL-6R antibody therapy reduced intestinal tumorigenesis in Apcmin/+Mlkl-/- mice. Notably, low MLKL expression in human colorectal tumors, which enhanced STAT3 activation, was associated with decreased overall survival. Together, our results reveal that MLKL exhibits a suppressive effect during intestinal tumorigenesis by suppressing the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signals.
Keywords: Anti-IL-6R antibody therapy.; IL-6/STAT3; Intestinal tumorigenesis; MLKL.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triptolide Inhibits Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines and Proliferation of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Induced by IL-6/sIL-6R-Mediated JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Curr Med Sci. 2021 Feb;41(1):133-139. doi: 10.1007/s11596-020-2302-1. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Curr Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33582917
-
Regulatory effect of calcineurin inhibitor, tacrolimus, on IL-6/sIL-6R-mediated RANKL expression through JAK2-STAT3-SOCS3 signaling pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013 Feb 13;15(1):R26. doi: 10.1186/ar4162. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 23406906 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin promotes apoptosis in a murine model of colorectal cancer by mechanisms involving downregulation of IL-6-STAT3 signaling pathway.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011 Jan;26(1):13-22. doi: 10.1007/s00384-010-1060-0. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011. PMID: 20886344
-
Resolvin D1 suppresses inflammation-associated tumorigenesis in the colon by inhibiting IL-6-induced mitotic spindle abnormality.FASEB J. 2021 May;35(5):e21432. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002392R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33794029
-
STAT3 and sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammation-associated colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10279-87. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10279. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Many Faces of MLKL, the Executor of Necroptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 14;24(12):10108. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210108. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Key Effector of Necroptotic Cell Death, MLKL, in Mouse Models of Disease.Biomolecules. 2021 May 28;11(6):803. doi: 10.3390/biom11060803. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34071602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RIPK3 Suppresses the Progression of Spontaneous Intestinal Tumorigenesis.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 30;11:664927. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.664927. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33996591 Free PMC article.
-
MLKL signaling regulates macrophage polarization in acute pancreatitis through CXCL10.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Feb 24;14(2):155. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05655-w. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36828808 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a Necroptosis Related Genes Signature to Predict Prognosis and Therapeutic Response in Colon Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 8;10:921320. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.921320. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35874811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC. et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:145–64. - PubMed
-
- Islami F, Goding Sauer A, Miller KD, Siegel RL, Fedewa SA, Jacobs EJ. et al. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:31–54. - PubMed
-
- Woolf SH. The best screening test for colorectal cancer-a personal choice. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1641–3. - PubMed
-
- Walsh JM, Terdiman JP. Colorectal cancer screening: scientific review. JAMA. 2003;289:1288–96. - PubMed
-
- Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao D. et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell. 2012;148:213–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

