Heat shock protein 90 promotes RNA helicase DDX5 accumulation and exacerbates hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting autophagy
- PMID: 33764710
- PMCID: PMC8330532
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0262
Heat shock protein 90 promotes RNA helicase DDX5 accumulation and exacerbates hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting autophagy
Abstract
Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the main type of liver cancer, has a high morbidity and mortality, and a poor prognosis. RNA helicase DDX5, which acts as a transcriptional co-regulator, is overexpressed in most malignant tumors and promotes cancer cell growth. Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) is an important molecular chaperone in the conformational maturation and stabilization of numerous proteins involved in cell growth or survival.
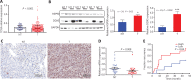
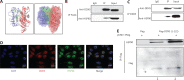
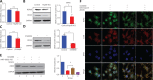
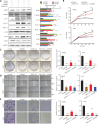
Methods: DDX5 mRNA and protein expression in surgically resected HCC tissues from 24 Asian patients were detected by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot, respectively. The interaction of DDX5-HSP90 was determined by molecular docking, immunoprecipitation, and laser scanning confocal microscopy. The autophagy signal was detected by Western blot. The cell functions and signaling pathways of DDX5 were determined in 2 HCC cell lines. Two different murine HCC xenograft models were used to determine the function of DDX5 and the therapeutic effect of an HSP90 inhibitor.
Results: HSP90 interacted directly with DDX5 and inhibited DDX5 protein degradation in the AMPK/ULK1-regulated autophagy pathway. The subsequent accumulation of DDX5 protein induced the malignant phenotype of HCC by activating the β-catenin signaling pathway. The silencing of DDX5 or treatment with HSP90 inhibitor both blocked in vivo tumor growth in a murine HCC xenograft model. High levels of HSP90 and DDX5 protein were associated with poor prognoses.
Conclusions: HSP90 interacted with DDX5 protein and subsequently protected DDX5 protein from AMPK/ULK1-regulated autophagic degradation. DDX5 and HSP90 are therefore potential therapeutic targets for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; RNA helicase DDX5; autophagy; heat shock protein 90; β-catenin pathway.
Copyright © 2021 Cancer Biology & Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DEAD Box Protein 5 Inhibits Liver Tumorigenesis by Stimulating Autophagy via Interaction with p62/SQSTM1.Hepatology. 2019 Mar;69(3):1046-1063. doi: 10.1002/hep.30300. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30281815 Free PMC article.
-
DDX5 promotes proliferation and tumorigenesis of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by activating β-catenin signaling pathway.Cancer Sci. 2015 Oct;106(10):1303-12. doi: 10.1111/cas.12755. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26212035 Free PMC article.
-
HSP90 inhibits apoptosis and promotes growth by regulating HIF-1α abundance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Mar;37(3):825-35. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2482. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26846697
-
The role of HSP90 molecular chaperones in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Dec;235(12):9110-9120. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29776. Epub 2020 May 26. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32452023 Review.
-
The Role of HSP90 and TRAP1 Targets on Treatment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 29. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01151-4. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38684604 Review.
Cited by
-
[MicroRNA-424 inhibits autophagy and proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ATG14].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Jul 20;41(7):1012-1021. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.07.07. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34308850 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Unraveling the Janus-Faced Role of Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications for Therapeutic Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 13;24(22):16255. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216255. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Action and function of helicases on RNA G-quadruplexes.Methods. 2022 Aug;204:110-125. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Methods. 2022. PMID: 34509630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting and regulation of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma: revisiting the molecular interactions and mechanisms for new therapy approaches.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Feb 9;21(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01053-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36759819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple functions of the DEAD-box RNA helicase, DDX5 (p68), make DDX5 a superior oncogenic biomarker and target for targeted cancer therapy.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Oct 15;11(10):5190-5213. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34765320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J, Pikarsky E, Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16018. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
