Thiopurines activate an antiviral unfolded protein response that blocks influenza A virus glycoprotein accumulation
- PMID: 33762409
- PMCID: PMC8139708
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00453-21
Thiopurines activate an antiviral unfolded protein response that blocks influenza A virus glycoprotein accumulation
Abstract
Influenza A viruses (IAVs) utilize host shutoff mechanisms to limit antiviral gene expression and redirect translation machinery to the synthesis of viral proteins. Previously, we showed that IAV replication is sensitive to protein synthesis inhibitors that block translation initiation and induce formation of cytoplasmic condensates of untranslated messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes called stress granules (SGs). In this study, using an image-based high-content screen, we identified two thiopurines, 6-thioguanine (6-TG) and 6-thioguanosine (6-TGo), that triggered SG formation in IAV-infected cells and blocked IAV replication in a dose-dependent manner without eliciting SG formation in uninfected cells. 6-TG and 6-TGo selectively disrupted the synthesis and maturation of IAV glycoproteins hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) without affecting the levels of the viral RNAs that encode them. By contrast, these thiopurines had minimal effect on other IAV proteins or the global host protein synthesis. Disruption of IAV glycoprotein accumulation by 6-TG and 6-TGo correlated with activation of unfolded protein response (UPR) sensors activating transcription factor-6 (ATF6), inositol requiring enzyme-1 (IRE1) and PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), leading to downstream UPR gene expression. Treatment of infected cells with the chemical chaperone 4-phenylbutyric acid diminished thiopurine-induced UPR activation and partially restored the processing and accumulation of HA and NA. By contrast, chemical inhibition of the integrated stress response downstream of PERK restored accumulation of NA monomers but did not restore processing of viral glycoproteins. Genetic deletion of PERK enhanced the antiviral effect of 6-TG without causing overt cytotoxicity, suggesting that while UPR activation correlates with diminished viral glycoprotein accumulation, PERK could limit the antiviral effects of drug-induced ER stress. Taken together, these data indicate that 6-TG and 6-TGo are effective host-targeted antivirals that trigger the UPR and selectively disrupt accumulation of viral glycoproteins.IMPORTANCESecreted and transmembrane proteins are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where they are folded and modified prior to transport. Many viruses rely on the ER for the synthesis and processing of viral glycoproteins that will ultimately be incorporated into viral envelopes. Viral burden on the ER can trigger the unfolded protein response (UPR). Much remains to be learned about how viruses co-opt the UPR to ensure efficient synthesis of viral glycoproteins. Here, we show that two FDA-approved thiopurine drugs, 6-TG and 6-TGo, induce the UPR, which represents a previously unrecognized effect of these drugs on cell physiology. This thiopurine-mediated UPR activation blocks influenza virus replication by impeding viral glycoprotein accumulation. Our findings suggest that 6-TG and 6-TGo may have broad antiviral effect against enveloped viruses that require precise tuning of the UPR to support viral glycoprotein synthesis.
Copyright © 2021 Slaine et al.
Figures
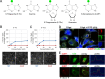
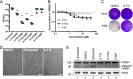
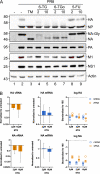
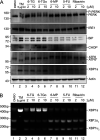

Similar articles
-
The Human Cytomegalovirus Endoplasmic Reticulum-Resident Glycoprotein UL148 Activates the Unfolded Protein Response.J Virol. 2018 Sep 26;92(20):e00896-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00896-18. Print 2018 Oct 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30045994 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Sensing of Influenza A Virus Hemagglutinin Glycoproteins by the Host Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress Pathway Triggers a Potent Antiviral Response via ER-Associated Protein Degradation.J Virol. 2017 Dec 14;92(1):e01690-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01690-17. Print 2018 Jan 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 29046440 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV activates unfolded protein response sensors but suppresses downstream transcriptional responses to support lytic replication.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Dec 2;15(12):e1008185. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008185. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31790507 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular unfolded protein response against viruses used in gene therapy.Front Microbiol. 2014 May 26;5:250. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00250. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24904562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Unfolded protein response: its role in physiology and physiopathology].Med Sci (Paris). 2007 Mar;23(3):291-6. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2007233291. Med Sci (Paris). 2007. PMID: 17349291 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Optimizing the Live Attenuated Influenza A Vaccine Backbone for High-Risk Patient Groups.J Virol. 2022 Oct 26;96(20):e0087122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00871-22. Epub 2022 Oct 3. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36190240 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Events Involved in Influenza A Virus-Induced Cell Death.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 7;12:797789. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.797789. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35069499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The battle for autophagy between host and influenza A virus.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):46-59. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.2014680. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 34967267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the Role of Paraoxonase-1 and Chemokine Ligand 2 (C-C motif) in Metabolic Alterations Linked to Inflammation and Disease. A 2021 Update.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 1;11(7):971. doi: 10.3390/biom11070971. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34356595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influenza A virus propagation requires the activation of the unfolded protein response and the accumulation of insoluble protein aggregates.iScience. 2024 Feb 2;27(3):109100. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109100. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38405606 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

