Virus-specific NK cell memory
- PMID: 33755720
- PMCID: PMC7992500
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20201731
Virus-specific NK cell memory
Abstract
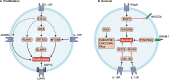
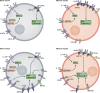
NK cells express a limited number of germline-encoded receptors that identify infected or transformed cells, eliciting cytotoxicity, effector cytokine production, and in some circumstances clonal proliferation and memory. To maximize the functional diversity of NK cells, the array and expression level of surface receptors vary between individual NK cell "clones" in mice and humans. Cytomegalovirus infection in both species can expand a population of NK cells expressing receptors critical to the clearance of infected cells and generate a long-lived memory pool capable of targeting future infection with greater efficacy. Here, we discuss the pathways and factors that regulate the generation and maintenance of effector and memory NK cells and propose how this understanding may be harnessed therapeutically.
© 2021 Sheppard and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytomegalovirus Infection Drives Avidity Selection of Natural Killer Cells.Immunity. 2019 Jun 18;50(6):1381-1390.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 May 15. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 31103381 Free PMC article.
-
NK cells generate memory-type responses to human cytomegalovirus-infected fibroblasts.Eur J Immunol. 2017 Jun;47(6):1032-1039. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646819. Epub 2017 May 23. Eur J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28475279
-
Impact of CMV Infection on Natural Killer Cell Clonal Repertoire in CMV-Naïve Rhesus Macaques.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 9;10:2381. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02381. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31649681 Free PMC article.
-
Memory responses of natural killer cells.Semin Immunol. 2017 Jun;31:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Semin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28863960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extrinsic and intrinsic drivers of natural killer cell clonality.Immunol Rev. 2024 May;323(1):80-106. doi: 10.1111/imr.13324. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38506411 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenomics of Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor (KIR) and HLA Class I: Coevolution and Consequences for Human Health.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022 Jul;10(7):1763-1775. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.04.036. Epub 2022 May 10. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022. PMID: 35561968 Free PMC article.
-
Differential IL-12 signaling induces human natural killer cell activating receptor-mediated ligand-specific expansion.J Exp Med. 2022 Aug 1;219(8):e20212434. doi: 10.1084/jem.20212434. Epub 2022 Jun 27. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35758909 Free PMC article.
-
(Auto)Antibody Responses Shape Memory NK Cell Pool Size and Composition.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 8;10(3):625. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030625. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327427 Free PMC article.
-
Process engineering of natural killer cell-based immunotherapy.Trends Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;41(10):1314-1326. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2023.03.018. Epub 2023 May 2. Trends Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37142447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic regulation of NK cell function: implications for immunotherapy.Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2023 Jan 23;5(1):e00020. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000020. eCollection 2023 Jan. Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2023. PMID: 36710923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams, N.M., Geary C.D., Santosa E.K., Lumaquin D., Le Luduec J.B., Sottile R., van der Ploeg K., Hsu J., Whitlock B.M., Jackson B.T., et al. . 2019. Cytomegalovirus Infection Drives Avidity Selection of Natural Killer Cells. Immunity. 50:1381–1390.e5. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.04.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aguilar, O.A., Berry R., Rahim M.M.A., Reichel J.J., Popović B., Tanaka M., Fu Z., Balaji G.R., Lau T.N.H., Tu M.M., et al. . 2017. A Viral Immunoevasin Controls Innate Immunity by Targeting the Prototypical Natural Killer Cell Receptor Family. Cell. 169:58–71.e14. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andoniou, C.E., van Dommelen S.L.H., Voigt V., Andrews D.M., Brizard G., Asselin-Paturel C., Delale T., Stacey K.J., Trinchieri G., and Degli-Esposti M.A.. 2005. Interaction between conventional dendritic cells and natural killer cells is integral to the activation of effective antiviral immunity. Nat. Immunol. 6:1011–1019. 10.1038/ni1244 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

