Can strain elastography be used in reclassification of indeterminate breast lesions in BIRADS lexicon?: A prospective study
- PMID: 33737779
- PMCID: PMC7954173
- DOI: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_425_19
Can strain elastography be used in reclassification of indeterminate breast lesions in BIRADS lexicon?: A prospective study
Abstract
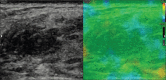
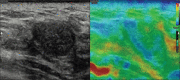
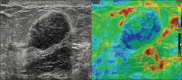
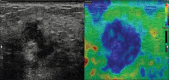
Purpose: To evaluate the role of strain elastography (SE) in reclassification of indeterminate breast lesions placed under BIRADS 3 and 4 categories by conventional ultrasound (US) parameters so as to recourse biopsy only for suspicious stiffer lesions.
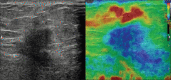
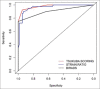
Methods: 113 breast lesions in 100 women assigned as BIRADS category 3 and 4 on US parameters were prospectively evaluated by SE followed by histo-pathological examination. Strain ratio (SR) and Elastography Score (ES) were determined for each lesion. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated for each modality and diagnostic performance were compared. The best cut-off point was calculated for each of the elastography parameter using the receiver operator curve analysis (ROC).
Results: Out of the 113 lesions, 40 were malignant (35.4%) and 73 were benign (64.6%). A statistically significant difference was observed in the AUC for ES and conventional US: 0.98 vs 0.90 (Difference = 0.08, P = 0.02). Elastography parameters were more specific as compared to US (ES-94.5 & SR-93.2% vs 63%, P < 0.05) with high NPV. SE performed better in BIRADS 4 category lesions. On the basis of elastography parameters, 85% of BIRADS 4 category lesions were correctly predicted as benign with overall sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic accuracy of elastography being 97%, 84.6% and 91.9%. Among BIRADS 3 category lesions, 97% were correctly predicted as benign and 50% lesions were correctly predicted as malignant with a sensitivity of 50%, specificity of 97.8% and diagnostic accuracy of 94%.
Conclusion: Strain elastography is a useful adjunct to conventional ultrasonography for the assessment of indeterminate breast lesions and may help in avoiding unnecessary follow ups and biopsies. Elastography score is a better parameter as compared to strain ratio.
Keywords: Breast cancer; elasticity score; strain elastography; strain ratio; ultrasonography.
Copyright: © 2021 Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Added value of strain elastography in the characterisation of breast lesions: A prospective study.Ultrasound. 2020 Aug;28(3):164-173. doi: 10.1177/1742271X20912762. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Ultrasound. 2020. PMID: 32831889 Free PMC article.
-
US-Elastography for Breast Lesion Characterization: Prospective Comparison of US BIRADS, Strain Elastography and Shear wave Elastography.Ultraschall Med. 2021 Oct;42(5):533-540. doi: 10.1055/a-1134-4937. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Ultraschall Med. 2021. PMID: 32330993 English.
-
Added Value of a New Strain Elastography Technique in Conventional Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Breast Masses: A Prospective Multicenter Study.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 9;11:779612. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.779612. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34858859 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of indeterminate focal breast lesions on grey-scale ultrasound: role of ultrasound elastography.Radiol Med. 2011 Oct;116(7):1027-38. doi: 10.1007/s11547-011-0648-y. Epub 2011 Mar 7. Radiol Med. 2011. PMID: 21424321 English, Italian.
-
Evaluating the role of strain ratio elastography in determining malignancy potential and calculating objective BIRADS US scores using ultrasonography and elastography features.Pol J Radiol. 2018 Jun 8;83:e268-e274. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2018.76790. eCollection 2018. Pol J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30627246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Malvia S, Bagadi S, Dubey U, Saxena S. Epidemiology of breast cancer in Indian women: Breast cancer epidemiology. Asia-Pacific J Clin Oncol. 2017;13:289–95. - PubMed
-
- Itoh A, Ueno E, Tohno E, Kamma H, Takahashi H, Shiina T, et al. Breast disease: Clinical application of us elastography for diagnosis. Radiology. 2006;239:341–50. - PubMed
-
- Ophir J, Céspedes I, Ponnekanti H, Yazdi Y, Li X. Elastography: A quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason Imaging. 1991;13:111–34. - PubMed
-
- Moon WK, Chang SC, Huang CS, Chang RF. Breast tumor classification using fuzzy clustering for breast elastography. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2011;37:700–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

