Reduction of prefrontal purinergic signaling is necessary for the analgesic effect of morphine
- PMID: 33733073
- PMCID: PMC7940985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102213
Reduction of prefrontal purinergic signaling is necessary for the analgesic effect of morphine
Abstract
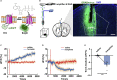
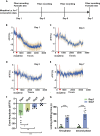
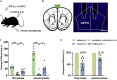
Morphine is commonly used to relieve moderate to severe pain, but repeated doses cause opioid tolerance. Here, we used ATP sensor and fiber photometry to detect prefrontal ATP level. It showed that prefrontal ATP level decreased after morphine injection and the event amplitude tended to decrease with continuous morphine exposure. Morphine had little effect on prefrontal ATP due to its tolerance. Therefore, we hypothesized that the analgesic effect of morphine might be related to ATP in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Moreover, local infusion of ATP partially antagonized morphine analgesia. Then we found that inhibiting P2X7R in the mPFC mimicked morphine analgesia. In morphine-tolerant mice, pretreatment with P2X4R or P2X7R antagonists in the mPFC enhanced analgesic effect. Our findings suggest that reduction of prefrontal purinergic signaling is necessary for the morphine analgesia, which help elucidate the mechanism of morphine analgesia and may lead to the development of new clinical treatments for neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Clinical Neuroscience; Molecular Neuroscience; Neuroscience.
© 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Median Nerve Stimulation as a Nonpharmacological Approach to Bypass Analgesic Tolerance to Morphine: A Proof-of-Concept Study in Mice.J Pain. 2021 Mar;22(3):300-312. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2020.09.003. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Pain. 2021. PMID: 33069869 Free PMC article.
-
A new potent analgesic agent with reduced liability to produce morphine tolerance.Brain Res Bull. 2015 Aug;117:32-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.07.005. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Brain Res Bull. 2015. PMID: 26235542
-
Site-Specific Regulation of P2X7 Receptor Function in Microglia Gates Morphine Analgesic Tolerance.J Neurosci. 2017 Oct 18;37(42):10154-10172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0852-17.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 18. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28924009 Free PMC article.
-
The plasticity of the association between mu-opioid receptor and glutamate ionotropic receptor N in opioid analgesic tolerance and neuropathic pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 15;716(1-3):94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.066. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23499699 Review.
-
[Development of opioid tolerance -- molecular mechanisms and clinical consequences].Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2003 Jan;38(1):14-26. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-36558. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2003. PMID: 12522725 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The Inflammation/NF-κB and BDNF/TrkB/CREB Pathways in the Cerebellum Are Implicated in the Changes in Spatial Working Memory After Both Morphine Dependence and Withdrawal in Rat.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):6721-6733. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03993-0. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38347284
-
Microglial inflammation modulates opioid analgesic tolerance.J Neurosci Res. 2023 Sep;101(9):1383-1392. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25199. Epub 2023 Apr 26. J Neurosci Res. 2023. PMID: 37186407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pain-related cortico-limbic plasticity and opioid signaling.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Jun 15;231:109510. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109510. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36944393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excitatory and inhibitory neuronal signaling in inflammatory and diabetic neuropathic pain.Mol Med. 2023 Apr 17;29(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00647-0. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37069517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purified Serum IgG from a Patient with Anti-IgLON5 Antibody Cause Long-Term Movement Disorders with Impaired Dopaminergic Pathways in Mice.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 7;11(9):2483. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092483. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brake A.J., Wagenbach M.J., Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994;371:519–523. - PubMed
-
- Bravo D., Maturana C.J., Pelissier T., Hernández A., Constandil L. Interactions of pannexin 1 with NMDA and P2X7 receptors in central nervous system pathologies: possible role on chronic pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2015;101:86–93. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G., Fredholm B.B., Verkhratsky A. Adenosine and ATP receptors in the brain. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2011;11:973–1011. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen. Pharmacol. 1985;16:433–440. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

