Using Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis to Identify Abnormally Methylated Differentially Expressed Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 33732011
- PMCID: PMC7956867
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S294505
Using Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis to Identify Abnormally Methylated Differentially Expressed Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: For the identification of abnormally methylated differentially expressed genes (MDEGs) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), this study integrated four microarray datasets to investigate the fundamental mechanisms of tumorigenesis.
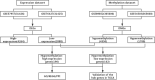
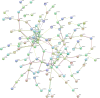
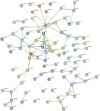
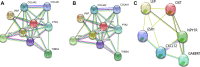
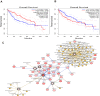
Methods: We obtained the expression (GSE76427, GSE57957) and methylation (GSE89852, GSE54503) profiles from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). The abnormally MDEGs were identified by using R software. We used the clusterProfiler package for the functional and pathway enrichment analysis. The String database was used to build the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and visualize it in Cytoscape. MCODE was employed in the module analysis. Additionally, Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) were employed to validate results. Lastly, we used cBioPortal software to examine the hub genetic alterations.
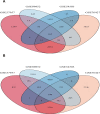
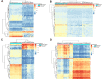
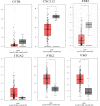
Results: We identified 162 hypermethylated, down-regulated genes and 190 hypomethylated, up-regulated genes. Up-regulated genes with low methylation were enriched in biological processes, such as keratinocyte proliferation, and calcium homeostasis. Pathway analysis was enriched in the AMPK and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. The PPI network identified PTK2, VWF, and ITGA2 as hypomethylated, high-expressing hub genes. Down-regulated genes with high methylation were related to responses to peptide hormones and estradiol, multi-multicellular organism process. Pathway analysis indicated enrichment in camp, oxytocin signaling pathways. The PPI network identified CFTR, ESR1, and CXCL12 as hypermethylated, low-expressing hub genes. Upon verification in TCGA databases, we found that the expression and methylation statuses of the hub genes changed significantly, and it was consistent with our results.
Conclusion: The novel abnormally MDEGs and pathways in HCC were identified. These results helped us further understand the molecular mechanisms underlying HCC invasion, metastasis, and development. Hub genes can serve as biomarkers for an accurate diagnosis and treatment of HCC, and PTK2, VWF, ITGA2, CFTR, ESR1, and CXCL12 are included.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; gene expression; hepatocellular carcinoma; hub genes; methylation.
© 2021 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that have no competing interests in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics analysis of aberrantly methylated-differentially expressed genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun 28;24(24):2605-2616. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i24.2605. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29962817 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics-Based Identification of Methylated-Differentially Expressed Genes and Related Pathways in Gastric Cancer.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Nov;62(11):3029-3039. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4740-6. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28914394
-
DNA methylation biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Sep 17;18:140. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0629-5. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30245591 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of aberrantly methylated differentially expressed genes in prostate carcinoma using integrated bioinformatics.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Mar 5;19:51. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0763-8. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 30872976 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 9;15(4):e0230524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230524. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32271791 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of core genes as promising diagnostic signature in hepatocellular carcinoma based on integrated bioinformatics approach.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 9;12(1):19072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22059-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36351994 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes Associated with the Prognosis and Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Oct 22;2022:4237633. doi: 10.1155/2022/4237633. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36317111 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

