Epigenetic reprogramming of host and viral genes by Human Cytomegalovirus infection in Kasumi-3 myeloid progenitor cells at early times post-infection
- PMID: 33731453
- PMCID: PMC10021080
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00183-21
Epigenetic reprogramming of host and viral genes by Human Cytomegalovirus infection in Kasumi-3 myeloid progenitor cells at early times post-infection
Abstract
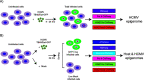
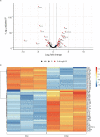
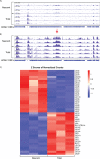
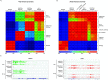
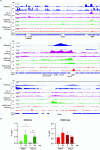
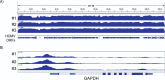
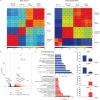
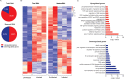
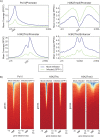
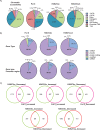
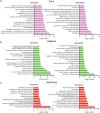
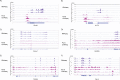
HCMV establishes latency in myeloid cells. Using the Kasumi-3 latency model, we previously showed that lytic gene expression is activated prior to establishment of latency in these cells. The early events in infection may have a critical role in shaping establishment of latency. Here, we have used an integrative multi-omics approach to investigate dynamic changes in host and HCMV gene expression and epigenomes at early times post infection. Our results show dynamic changes in viral gene expression and viral chromatin. Analyses of Pol II, H3K27Ac and H3K27me3 occupancy of the viral genome showed that 1) Pol II occupancy was highest at the MIEP at 4 hours post infection. However, it was observed throughout the genome; 2) At 24 hours, H3K27Ac was localized to the major immediate early promoter/enhancer and to a possible second enhancer in the origin of replication OriLyt; 3) viral chromatin was broadly accessible at 24 hpi. In addition, although HCMV infection activated expression of some host genes, we observed an overall loss of de novo transcription. This was associated with loss of promoter-proximal Pol II and H3K27Ac, but not with changes in chromatin accessibility or a switch in modification of H3K27.Importance.HCMV is an important human pathogen in immunocompromised hosts and developing fetuses. Current anti-viral therapies are limited by toxicity and emergence of resistant strains. Our studies highlight emerging concepts that challenge current paradigms of regulation of HCMV gene expression in myeloid cells. In addition, our studies show that HCMV has a profound effect on de novo transcription and the cellular epigenome. These results may have implications for mechanisms of viral pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human Cytomegalovirus IE2 Both Activates and Represses Initiation and Modulates Elongation in a Context-Dependent Manner.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0033722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00337-22. Epub 2022 May 17. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35579393 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Role for the Human Cytomegalovirus Major Immediate Early Proteins in Recruitment of RNA Polymerase II and H3K27Ac To an Enhancer-Like Element in OriLyt.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0314422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03144-22. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36645269 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin structure regulates human cytomegalovirus gene expression during latency, reactivation and lytic infection.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Mar-Apr;1799(3-4):286-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.08.001. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19682613 Review.
-
Chromatin-mediated regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression.Virus Res. 2011 May;157(2):134-43. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.09.019. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20875471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Induces Reactivation of Human Cytomegalovirus Independently of Myeloid Cell Differentiation following Posttranscriptional Establishment of Latency.mBio. 2018 Sep 11;9(5):e01560-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01560-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30206173 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Human Cytomegalovirus IE2 Both Activates and Represses Initiation and Modulates Elongation in a Context-Dependent Manner.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0033722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00337-22. Epub 2022 May 17. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35579393 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus infection coopts chromatin organization to diminish TEAD1 transcription factor activity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 22:2024.04.12.588762. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.12.588762. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38645179 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Hematopoietic stem cells and betaherpesvirus latency.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jun 6;13:1189805. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1189805. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37346032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal dynamics of HCMV gene expression in lytic and latent infections.Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 12;39(2):110653. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110653. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35417700 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Role for the Human Cytomegalovirus Major Immediate Early Proteins in Recruitment of RNA Polymerase II and H3K27Ac To an Enhancer-Like Element in OriLyt.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0314422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03144-22. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36645269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kondo K, Mocarski ES. 1995. Cytomegalovirus latency and latency-specific transcription in hematopoietic progenitors. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl 99:63–67. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

