Impact of Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor Blockade on Resiniferatoxin-Induced Neuropathy
- PMID: 33727914
- PMCID: PMC7937473
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8854461
Impact of Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor Blockade on Resiniferatoxin-Induced Neuropathy
Abstract
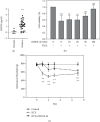
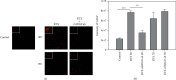
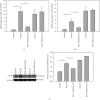
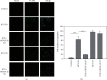
Resiniferatoxin is an ultrapotent capsaicin analog that mediates nociceptive processing; treatment with resiniferatoxin can cause an inflammatory response and, ultimately, neuropathic pain. Hepatoma-derived growth factor, a growth factor related to normal development, is associated with neurotransmitters surrounding neurons and glial cells. Therefore, the study aims to investigate how blocking hepatoma-derived growth factor affects the inflammatory response in neuropathic pain. Serum hepatoma-derived growth factor protein expression was measured via ELISA. Resiniferatoxin was administrated intraperitoneally to induce neuropathic pain in 36 male Sprague-Dawley rats which were divided into three groups (resiniferatoxin+recombinant hepatoma-derived growth factor antibody group, resiniferatoxin group, and control group) (n = 12/group). The mechanical threshold response was tested with calibration forceps. Cell apoptosis was measured by TUNEL assay. Immunofluorescence staining was performed to detect apoptosis of neuron cells and proliferation of astrocytes in the spinal cord dorsal horn. RT-PCR technique and western blot were used to measure detect inflammatory factors and protein expressions. Serum hepatoma-derived growth factor protein expression was higher in the patients with sciatica compared to controls. In resiniferatoxin-group rats, protein expression of hepatoma-derived growth factor was higher than controls. Blocking hepatoma-derived growth factor improved the mechanical threshold response in rats. In dorsal root ganglion, blocking hepatoma-derived growth factor inhibited inflammatory cytokines. In the spinal cord dorsal horn, blocking hepatoma-derived growth factor inhibited proliferation of astrocyte, apoptosis of neuron cells, and attenuated expressions of pain-associated proteins. The experiment showed that blocking hepatoma-derived growth factor can prevent neuropathic pain and may be a useful alternative to conventional analgesics.
Copyright © 2021 Chieh-Hsin Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor redistribution in the dorsal root ganglia correlates with neuropathic pain inhibition after resiniferatoxin treatment.Spine J. 2010 Aug;10(8):715-20. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2010.03.029. Epub 2010 May 7. Spine J. 2010. PMID: 20452292
-
Puerarin alleviates vincristine-induced neuropathic pain and neuroinflammation via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB and activation of the TGF-β/Smad pathway in rats.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Dec;89(Pt B):107060. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107060. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33049496
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta regulates glial glutamate transporter protein expression in the spinal dorsal horn in rats with neuropathic pain.Exp Neurol. 2014 Feb;252:18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.11.018. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24275526 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of resiniferatoxin binding sites on sensory neurons: co-regulation of resiniferatoxin binding and capsaicin sensitivity in adult rat dorsal root ganglia.Neuroscience. 1993 Dec;57(3):747-57. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90021-7. Neuroscience. 1993. PMID: 8309534
-
The Different Dynamic Changes of Nerve Growth Factor in the Dorsal Horn and Dorsal Root Ganglion Leads to Hyperalgesia and Allodynia in Diabetic Neuropathic Pain.Pain Physician. 2017 May;20(4):E551-E561. Pain Physician. 2017. PMID: 28535564
Cited by
-
RTA-408 Regulates p-NF-κB/TSLP/STAT5 Signaling to Ameliorate Nociceptive Hypersensitivity in Chronic Constriction Injury Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Mar;61(3):1714-1725. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03660-w. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37773082
-
The Contribution of TSLP Activation to Hyperalgesia in Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons of a Rat.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 11;23(4):2012. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042012. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216130 Free PMC article.
-
CDDO regulates central and peripheral sensitization to attenuate post-herpetic neuralgia by targeting TRPV1/PKC-δ/p-Akt signals.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Mar;28(6):e18131. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18131. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38426931 Free PMC article.
-
Linalyl Acetate Ameliorates Mechanical Hyperalgesia Through Suppressing Inflammation by TSLP/IL-33 Signaling.Neurochem Res. 2022 Dec;47(12):3805-3816. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03763-1. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 36287299 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Expression of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Chronic Constriction Injury of Rat Nerve.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7105. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137105. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281158 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

