Downregulation of Zn-transporters along with Fe and redox imbalance causes growth and photosynthetic disturbance in Zn-deficient tomato
- PMID: 33727682
- PMCID: PMC7966403
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85649-w
Downregulation of Zn-transporters along with Fe and redox imbalance causes growth and photosynthetic disturbance in Zn-deficient tomato
Abstract
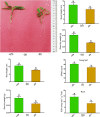
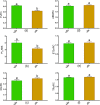
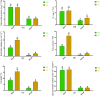
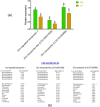
Zinc (Zn) deficiency hinders growth and development in tomato. This study unveils the responses of how Zn starvation affects physiological and molecular processes in tomato. Zn deficiency negatively affected the biomass, cellular integrity, and chlorophyll synthesis in tomato. Also, Zn deficiency decreased the maximum yield of PSII, photosynthesis performance index and dissipation energy per active reaction center, although the antenna size, trapping energy efficiency and electron transport flux were stable in Zn-starved leaves. Further, Zn shortage caused a substantial reduction in Zn and Fe concentrations in both roots and shoots along with decreased root Fe-reductase activity accompanied by the downregulation of Fe-regulated transporter 1, Zn transporter-like (LOC100037509), and Zn transporter (LOC101255999) genes predicted to be localized in the root plasma membrane. The interactome partners of these Zn transporters are predominantly associated with root-specific metal transporter, ferric-chelate reductase, BHLH transcriptional regulator, and Zn metal ion transporters, suggesting that Zn homeostasis may be tightly linked to the Fe status along with BHLH transcription factor in Zn-deficient tomato. We also noticed elevated O2.- and H2O2 due to Zn deficiency which was consistent with the inefficient antioxidant properties. These findings will be useful in the downstream approach to improve vegetable crops sensitive to Zn-deficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Morpho-physiological retardations due to iron toxicity involve redox imbalance rather than photosynthetic damages in tomato.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2020 Nov;156:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.08.034. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32906022
-
Molecular characterization of Fe-acquisition genes causing decreased Fe uptake and photosynthetic inefficiency in Fe-deficient sunflower.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 10;11(1):5537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85147-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33692433 Free PMC article.
-
Sulphur deprivation limits Fe-deficiency responses in tomato plants.Planta. 2009 Jun;230(1):85-94. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-0919-1. Epub 2009 Apr 7. Planta. 2009. PMID: 19350269
-
Identification of nutrient deficiency in maize and tomato plants by in vivo chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 Aug;81:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.03.029. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24811616
-
Iron deprivation results in a rapid but not sustained increase of the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism and sulfate uptake in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) seedlings.J Integr Plant Biol. 2014 Jan;56(1):88-100. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12110. Epub 2013 Nov 25. J Integr Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24119307
Cited by
-
Zinc biofortification potential of diverse mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] genotypes under field conditions.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 23;16(6):e0253085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253085. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2022 Nov 16;17(11):e0277596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277596 PMID: 34161364 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Integration of the Metabolomic and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Remarkable Compounds of G. bicolor Young and Mature Leaves under Different Iron Nutrient Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 21;23(3):1160. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031160. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163082 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc toxicity response in Ceratoides arborescens and identification of CaMTP, a novel zinc transporter.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 6;13:976311. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.976311. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36161019 Free PMC article.
-
Azospirillum brasilense and Zinc Rates Effect on Fungal Root Colonization and Yield of Wheat-Maize in Tropical Savannah Conditions.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;11(22):3154. doi: 10.3390/plants11223154. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432883 Free PMC article.
-
Foliar Sprayed Green Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Mitigate Drought-Induced Oxidative Stress in Tomato.Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 7;10(11):2400. doi: 10.3390/plants10112400. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34834763 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

