Icaritin Induces Anti-tumor Immune Responses in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inhibiting Splenic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Generation
- PMID: 33717093
- PMCID: PMC7952329
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.609295
Icaritin Induces Anti-tumor Immune Responses in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inhibiting Splenic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Generation
Abstract
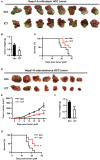
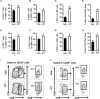
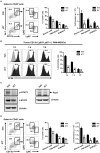
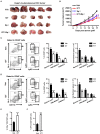
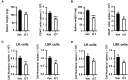
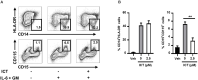
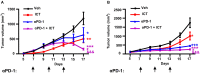
Recent studies have demonstrated that splenic extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH) is an important mechanism for the accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in tumor tissues, and thus contributes to disease progression. Icaritin, a prenylflavonoid derivative from plants of the Epimedium genus, has been implicated as a novel immune-modulator that could prolong the survival of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. However, it is unclear whether icaritin achieves its anti-tumor effects via the regulation of MDSCs generated by EMH in HCC. Here, we investigated the anti-tumor potential of icaritin and its mechanism of action in murine HCC. Icaritin suppressed tumor progression and significantly prolonged the survival of mice-bearing orthotopic and subcutaneous HCC tumors. Rather than exerting direct cytotoxic activity against tumor cells, icaritin significantly reduced the accumulation and activation of tumoral and splenic MDSCs, and increased the number and activity of cytotoxic T cells. Mechanistically, icaritin downregulates the tumor-associated splenic EMH, thereby reducing the generation and activation of MDSCs. The inhibitory effects of icaritin on human MDSCs in vitro were verified in short-term culture with cord-blood derived hematopoietic precursors. Furthermore, icaritin synergistically enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade therapy in HCC mice. These findings revealed that icaritin dampens tumoral immunosuppression to elicit anti-tumor immune responses by preventing MDSC generation via the attenuation of EMH. Thus, icaritin may serve as a novel adjuvant or even a stand-alone therapeutic agent for the effective treatment of HCC.
Keywords: MDSC; extramedullary hematopoiesis; hepatocellular carcinoma; icaritin; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2021 Tao, Liu, Wang, Luo, Xu, Ye, Zheng, Meng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
BY and KM are employees of Beijing Shenogen Biomedical Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Icaritin-induced immunomodulatory efficacy in advanced hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Immunodynamic biomarkers and overall survival.Cancer Sci. 2020 Nov;111(11):4218-4231. doi: 10.1111/cas.14641. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32889778 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the crosstalk between cytokine-induced killer cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2019 Mar;70(3):449-457. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.040. Epub 2018 Nov 9. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30414862 Free PMC article.
-
Icaritin promotes tumor T-cell infiltration and induces antitumor immunity in mice.Eur J Immunol. 2019 Dec;49(12):2235-2244. doi: 10.1002/eji.201948225. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Eur J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31465113
-
New insights into the anticancer therapeutic potential of icaritin and its synthetic derivatives.Drug Dev Res. 2024 Apr;85(2):e22175. doi: 10.1002/ddr.22175. Drug Dev Res. 2024. PMID: 38567708 Review.
-
Current perspectives on the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and opportunities.Mol Cancer. 2019 Aug 29;18(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1047-6. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31464625 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Nutrients Regulating Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells in Cancer: A Scoping Review.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Aug 23;46(9):9286-9297. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090549. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Icaritin Exerts Anti-Cancer Effects through Modulating Pyroptosis and Immune Activities in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 21;12(8):1917. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081917. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200381 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cancers of hepatobiliary system: from clinical evidence to drug discovery.Mol Cancer. 2024 Oct 1;23(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02136-2. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39354529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-associated myeloid cells in cancer immunotherapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jul 6;16(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01473-x. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37415162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-CSF/GM-CSF-induced hematopoietic dysregulation in the progression of solid tumors.FEBS Open Bio. 2022 Jul;12(7):1268-1285. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13445. Epub 2022 Jun 9. FEBS Open Bio. 2022. PMID: 35612789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

