Elevated Lactate by High-Intensity Interval Training Regulates the Hippocampal BDNF Expression and the Mitochondrial Quality Control System
- PMID: 33716776
- PMCID: PMC7946986
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.629914
Elevated Lactate by High-Intensity Interval Training Regulates the Hippocampal BDNF Expression and the Mitochondrial Quality Control System
Abstract
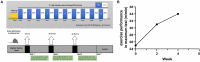
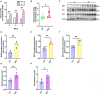
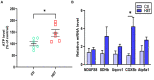
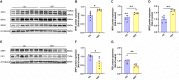
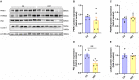
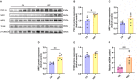
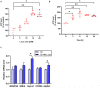
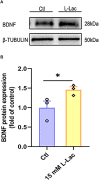
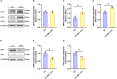
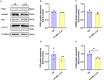
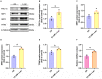
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is reported to be beneficial to brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) biosynthesis. A key element in this may be the existence of lactate, the most obvious metabolic product of exercise. In vivo, this study investigated the effects of a 6-week HIIT on the peripheral and central lactate changes, mitochondrial quality control system, mitochondrial function and BDNF expression in mouse hippocampus. In vitro, primary cultured mice hippocampal cells were used to investigate the role and the underlying mechanisms of lactate in promoting mitochondrial function during HIIT. In vivo studies, we firstly reported that HIIT can potentiate mitochondrial function [boost some of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) genes expression and ATP production], stimulate BDNF expression in mouse hippocampus along with regulating the mitochondrial quality control system in terms of promoting mitochondrial fusion and biogenesis, and suppressing mitochondrial fission. In parallel to this, the peripheral and central lactate levels elevated immediately after the training. In vitro study, our results revealed that lactate was in charge of regulating mitochondrial quality control system for mitochondrial function and thus may contribute to BDNF expression. In conclusion, our study provided the mitochondrial mechanisms of HIIT enhancing brain function, and that lactate itself can mediate the HIIT effect on mitochondrial quality control system in the hippocampus.
Keywords: BDNF; High-intensity interval training; lactate; mitochondrial quality control system; mouse hippocampus.
Copyright © 2021 Hu, Cai, Shang, Li, Feng, Liu, Xue and Lou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lactate Mediates High-Intensity Interval Training-Induced Promotion of Hippocampal Mitochondrial Function through the GPR81-ERK1/2 Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 7;12(12):2087. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122087. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136207 Free PMC article.
-
High intensity interval training induces dysregulation of mitochondrial respiratory complex and mitophagy in the hippocampus of middle-aged mice.Behav Brain Res. 2021 Aug 27;412:113384. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113384. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Behav Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 34147565
-
The effects of long-term lactate and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on brain neuroplasticity of aged mice.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 10;10(2):e24421. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24421. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38293399 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Universal Application of High-intensity Interval Training from Athletes and Sports Lovers to Patients.Keio J Med. 2017 Jun 25;66(2):19-24. doi: 10.2302/kjm.2016-0006-IR. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Keio J Med. 2017. PMID: 27498746 Review.
-
Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training Versus Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training On Blood Pressure in Adults with Pre- to Established Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials.Sports Med. 2018 Sep;48(9):2127-2142. doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-0944-y. Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 29949110 Review.
Cited by
-
The mitochondrial quality control system: a new target for exercise therapeutic intervention in the treatment of brain insulin resistance-induced neurodegeneration in obesity.Int J Obes (Lond). 2024 Jun;48(6):749-763. doi: 10.1038/s41366-024-01490-x. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Int J Obes (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38379083 Review.
-
High-intensity interval training reduces Tau and beta-amyloid accumulation by improving lactate-dependent mitophagy in rats with type 2 diabetes.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(11):1430-1439. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.77038.16664. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39386233 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate and Lactylation in the Brain: Current Progress and Perspectives.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Aug;43(6):2541-2555. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01335-7. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36928470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactate as Potential Mediators for Exercise-Induced Positive Effects on Neuroplasticity and Cerebrovascular Plasticity.Front Physiol. 2021 Jul 5;12:656455. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.656455. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34290615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential mechanisms of lactate in mediating exercise-enhanced cognitive function: a dual role as an energy supply substrate and a signaling molecule.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2022 Jul 30;19(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12986-022-00687-z. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35907984 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

