Application of Nanobiotechnology for Early Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33710356
- PMCID: PMC7952259
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-021-11197-y
Application of Nanobiotechnology for Early Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
A most discussed topic of the new decade, COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by the recently discovered SARS-CoV-2. With an exceedingly high transmission rate, COVID-19 has affected almost all the countries in the world. Absent any vaccine or specific treatment, the humanity is left with nothing but the legacy method of quarantine. However, quarantine can only be effective when combined with early diagnosis of suspected cases. With their high sensitivity and unmatched specificity, biosensors have become an area of interest for development of novel diagnostic methods. Compared to the more traditional diagnostics, nanobiotechnology introduces biosensors as different diagnostics with greater versatility in application. Today, a growing number of analytes are being accurately identified by these nanoscopic sensing machines. Several reports of validated application with real samples further strengthen this idea. As of recent, there has been a rise in the number of studies on portable biosensors. Despite the slow progression, certain devices with embedded biosensors have managed to be of diagnostic value in several countries. The perceptible increase in development of mobile platforms has revolutionized the healthcare delivery system in the new millennium. The present article reviews the most recent advancements in development of diagnostic nanobiosensors and their application in the clinical fields. KEY POINTS: • There is no specific treatment for highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2. • Early diagnosis is critical for control of pandemic. • Highly sensitive/specific nanobiosensors are emerging assets against COVID-19.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; Biosensor; COVID-19; Early diagnosis; Nanobiotechnology; Pandemic; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
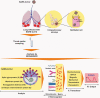
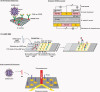
Similar articles
-
Clinical Utility of Biosensing Platforms for Confirmation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 May 24;11(6):167. doi: 10.3390/bios11060167. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Future developments in biosensors for field-ready SARS-CoV-2 virus diagnostics.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2021 Aug;68(4):695-699. doi: 10.1002/bab.2033. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32970352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isothermal amplification-assisted diagnostics for COVID-19.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Jun 1;205:114101. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114101. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 35202984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered two-dimensional nanomaterials based diagnostics integrated with internet of medical things (IoMT) for COVID-19.Chem Soc Rev. 2024 Apr 22;53(8):3774-3828. doi: 10.1039/d3cs00719g. Chem Soc Rev. 2024. PMID: 38433614 Review.
-
Biosensors as a future diagnostic approach for COVID-19.Life Sci. 2021 May 15;273:119117. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119117. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33508293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers: A Review.Materials (Basel). 2021 Jul 2;14(13):3706. doi: 10.3390/ma14133706. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34279276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
siRNA-based nanotherapeutics as emerging modalities for immune-mediated diseases: A preliminary review.Cell Biol Int. 2022 Sep;46(9):1320-1344. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11841. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Cell Biol Int. 2022. PMID: 35830711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the use of inorganic nanomaterials as anti caries agents.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 8;9(4):e15326. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15326. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37113794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New approach in SARS-CoV-2 surveillance using biosensor technology: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jan;29(2):1677-1695. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17096-z. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34689274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances of Representative Optical Biosensors for Rapid and Sensitive Diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 12;12(10):862. doi: 10.3390/bios12100862. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akbarzadeh A, Fekri Aval S, Sheervalilou R, Fekri L, Zarghami N, Mohammadian MJRCB, Medicine M. Quantum dots for biomedical delivery applications. Rev Cell Biol Mol Med. 2006;2(4):66–78.
-
- Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Duyne RP (2010) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nanoscience and Technology: A Collection of Reviews from Nature Journals. World Sci pp 308-319 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

