The Herbal Cocktail GSYJ Attenuated Airway Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in a Chronic Asthmatic Mouse Model
- PMID: 33708257
- PMCID: PMC7932788
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6691475
The Herbal Cocktail GSYJ Attenuated Airway Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in a Chronic Asthmatic Mouse Model
Abstract
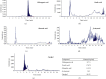
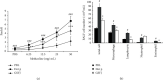
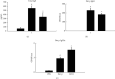
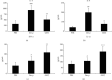
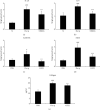
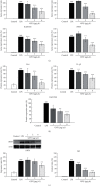
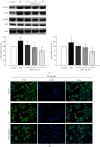
This study explored the potential therapeutic efficacy of GSYJ in attenuating asthma symptom severity and aimed to determine the immunomodulatory mechanism of GSYJ. A mouse model of chronic asthma induced by repeated Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Der p) challenge was established. In addition, 30 minutes before Der p challenge, the mice were orally administered GSYJ (1 g/kg). The mice were sacrificed to evaluate inflammatory cell infiltration, collagen deposition in the lung, total IgE in serum, and expression profiles of various cytokines in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and various genes in lung tissue. Furthermore, 30 minutes after the addition of GSYJ to RAW264.7 cell cultures, 100 ng/ml LPS was added to evaluate the effect of the drug on the LPS-induced expression of genes, proteins, and transcription factors. GSYJ may regulate transcription factors (cJUN/IRF3/NF-κB) to decrease the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, RANTES, and iNOS in macrophages and affect the IL-12, IFN-γ, IL-5, and IL-6 levels in the BALF of mice to relieve asthma symptoms, such as inflammatory cell infiltration, hyperresponsiveness, and increased serum total IgE levels. Therefore, GSYJ has the potential to be developed into a drug treatment for chronic asthma.
Copyright © 2021 Chung-Jen Chiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DFSG, a novel herbal cocktail with anti-asthma activity, suppressed MUC5AC in A549 cells and alleviated allergic airway hypersensitivity and inflammatory cell infiltration in a chronic asthma mouse model.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109584. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109584. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31766098
-
Xiao-Qing-Long-Tang attenuates allergic airway inflammation and remodeling in repetitive Dermatogoides pteronyssinus challenged chronic asthmatic mice model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jul 13;142(2):531-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.05.033. Epub 2012 Jun 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22658987
-
[A specific immune therapeutic effect of Der p2 T cell epitope vaccine on asthma mice].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 12;29(1):59-63. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2016120. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29469388 Chinese.
-
[Experimental study on the Der f 1 mRNA molecules derived from dermatophagoides farinae for specific immunotherapy on murine model of asthma].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;32(4):268-73. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25518589 Chinese.
-
Evaluation on the immunotherapy efficacies of synthetic peptide vaccines in asthmatic mice with group I and II allergens from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Nov 15;8(11):20402-12. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26884956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Vital signs: asthma prevalence, disease characteristics, and self-management education: United States, 2001-2009. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 2011;60(17):547–552. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

