Radiotherapy combined with nimotuzumab for elderly esophageal cancer patients: A phase II clinical trial
- PMID: 33707928
- PMCID: PMC7941689
- DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2021.01.06
Radiotherapy combined with nimotuzumab for elderly esophageal cancer patients: A phase II clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the safety and efficacy of nimotuzumab combined with radiotherapy for elderly patients with non-resectable esophageal carcinoma (EC).
Methods: Eligible patients were aged 70 years or older and had treatment-naïve, histologically proven inoperable locally advanced EC. Enrolled patients received radiotherapy with a total dose of 50-60 Gy in 25-30 fractions, concurrent with weekly infusion of nimotuzumab. The primary end point was the rate of more than grade 3 toxicities.
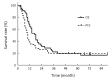
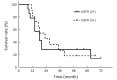
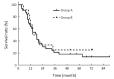
Results: From June 2011 to July 2016, 46 patients with stage II-IV EC with a median age of 76.5 years were enrolled. There were 10, 28 and 8 patients with stage II, III and IV disease, respectively. The common acute toxicities included esophagitis (grade 1-2, 75.4%; grade 3, 8.7%), pneumonitis (grade 1, 4.3%; grade 2, 6.5%; grade 3, 2.2%), leukopenia (grade 1-2, 60.9%; grade 3-4, 4.4%), gastrointestinal reaction (grade 1-2, 17.3%; grade 3, 2.2%), thrombocytopenia (grade 1-2, 21.7%; grade 3, 2.2%), and radiothermitis (grade 1-2, 39.2%). The incidence of grade 3-4 adverse effects was 17.4%. No grade 5 toxicities were observed. Clinical complete response, partial response, stable disease, and progressive disease were observed in 1 (2.2%), 31 (67.4%), 12 (26.1%), and 2 (4.3%) patients, respectively. The median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were 17 and 10 months, respectively. The 2-, 3-, and 5-year OS and PFS rates were 30.4%, 21.7%, 19.6%, and 26.1%, 19.6%, 19.6%, respectively.
Conclusions: Nimotuzumab combined with radiotherapy is a safe and effective therapy for elderly patients who are not surgical candidates. Further studies are warranted to confirm its therapeutic effects in elderly EC patients.
Keywords: Nimotuzumab; elderly; esophageal neoplasm; radiotherapy; treatment outcome.
Copyright © 2021 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy analysis of chemoradiotherapy/radiotherapy combined with nimotuzumab for treating unresectable oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma in elderly patients: a retrospective analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec 17;22(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02602-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36528571 Free PMC article.
-
Nimotuzumab combined with radiotherapy for esophageal cancer: preliminary study of a Phase II clinical trial.Onco Targets Ther. 2013 Nov 6;6:1589-96. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S50945. eCollection 2013. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 24235844 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy Combined with Nimotuzumab in Elderly Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Prospective Real-world Pragmatic Study.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2023;23(8):653-662. doi: 10.2174/1568009623666230315145937. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 36924100 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I study evaluating combined nimotuzumab and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery in locally advanced esophageal cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 Nov;84(5):1115-1123. doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03944-w. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31502113 Clinical Trial.
-
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: preclinical and early clinical data.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004 Feb;18(1):41-53. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8588(03)00138-2. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15005280 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Targeted Agents Combined With Chemoradiotherapy for the Treatment of Esophageal Cancer: A Network Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 29;11:621917. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.621917. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34912696 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy analysis of chemoradiotherapy/radiotherapy combined with nimotuzumab for treating unresectable oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma in elderly patients: a retrospective analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec 17;22(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02602-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36528571 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous integrated boost intensity-modulated radiotherapy (SIB-IMRT) combined with nimotuzumab for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC): A phase II clinical trial.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jun 4;24(1):679. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12427-y. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38831450 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development of a prognostic nomogram and risk stratification system for upper thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 12;13:1059539. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1059539. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37124485 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
