Changing trends of disease burden of gastric cancer in China from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions: Findings from Global Burden of Disease Study
- PMID: 33707924
- PMCID: PMC7941685
- DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2021.01.02
Changing trends of disease burden of gastric cancer in China from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions: Findings from Global Burden of Disease Study
Abstract
Objective: China is one of the countries with the heaviest burden of gastric cancer (GC) in the world. Understanding the epidemiological trends and patterns of GC in China can contribute to formulating effective prevention strategies.
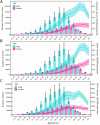
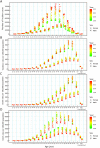
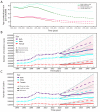
Methods: The data on incidence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) of GC in China from 1990 to 2019 were obtained from the Global Burden of Disease Study (2019). The estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) was calculated to evaluate the temporal trends of disease burden of GC, and the package Nordpred in the R program was used to perform an age-period-cohort analysis to predict the numbers and rates of incidence and mortality in the next 25 years.
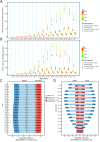
Results: The number of incident cases of GC increased from 317.34 thousand in 1990 to 612.82 thousand in 2019, while the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of GC decreased from 37.56 per 100,000 in 1990 to 30.64 per 100,000 in 2019, with an EAPC of -0.41 [95% confidence interval (95% CI): -0.77, -0.06]. Pronounced temporal trends in mortality and DALYs of GC were observed. In the next 25 years, the numbers of new GC cases and deaths are expected to increase to 738.79 thousand and 454.80 thousand, respectively, while the rates of incidence and deaths should steadily decrease. The deaths and DALYs attributable to smoking were different for males and females.
Conclusions: In China, despite the fact that the rates of GC have decreased during the past three decades, the numbers of new GC cases and deaths increased, and will continue to increase in the next 25 years. Additional strategies are needed to reduce the burden of GC, such as screening and early detection, novel treatments, and the prevention of risk factors.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; disease burden; prediction; risk factor; temporal trend.
Copyright © 2021 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changing trends of disease burden of stroke from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions among the Chinese population.Front Neurol. 2023 Oct 4;14:1255524. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1255524. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37869143 Free PMC article.
-
Changing trends of the disease burden of non-rheumatic valvular heart disease in China from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions: Findings from global burden of disease study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 19;9:912661. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.912661. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36741848 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of pancreatic cancer along with attributable risk factors in China from 1990 to 2019, and projections until 2030.Pancreatology. 2022 Jun;22(5):608-618. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2022.04.011. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Pancreatology. 2022. PMID: 35513974
-
The global burden and trends of four major types of heart disease, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Public Health. 2023 Jul;220:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 May 12. Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37182373 Review.
-
Updates on global epidemiology, risk and prognostic factors of gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 28;29(16):2452-2468. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2452. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37179585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Study to Investigate the Tumor-Suppressive Role of Radix Bupleuri on Gastric Cancer with Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Feb 8;18:375-394. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S441126. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 38347958 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the global research landscape on nutritional support for patients with gastrointestinal malignancy: visualization analysis.Support Care Cancer. 2023 Feb 22;31(3):179. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-07645-2. Support Care Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36810807 Review.
-
Disease Burden of Total and Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer in China from 1990 to 2019 and Predictions of Cancer Incidence and Mortality.Clin Epidemiol. 2023 Feb 1;15:151-163. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S391058. eCollection 2023. Clin Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 36755975 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal trend of gastric cancer burden along with its risk factors in China from 1990 to 2019, and projections until 2030: comparison with Japan, South Korea, and Mongolia.Biomark Res. 2021 Nov 16;9(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00340-6. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 34784961 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden of pertussis in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.BMC Public Health. 2024 May 30;24(1):1453. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18968-y. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38816714 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
International Agency for Research on Cancer. The Global Cancer Observatory. Cancer Today. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
