Super-resolution mapping of cellular double-strand break resection complexes during homologous recombination
- PMID: 33707212
- PMCID: PMC7980414
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2021963118
Super-resolution mapping of cellular double-strand break resection complexes during homologous recombination
Abstract
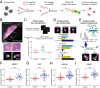
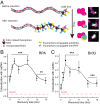
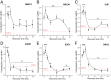
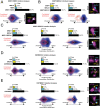
Homologous recombination (HR) is a major pathway for repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). The initial step that drives the HR process is resection of DNA at the DSB, during which a multitude of nucleases, mediators, and signaling proteins accumulates at the damage foci in a manner that remains elusive. Using single-molecule localization super-resolution (SR) imaging assays, we specifically visualize the spatiotemporal behavior of key mediator and nuclease proteins as they resect DNA at single-ended double-strand breaks (seDSBs) formed at collapsed replication forks. By characterizing these associations, we reveal the in vivo dynamics of resection complexes involved in generating the long single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) overhang prior to homology search. We show that 53BP1, a protein known to antagonize HR, is recruited to seDSB foci during early resection but is spatially separated from repair activities. Contemporaneously, CtBP-interacting protein (CtIP) and MRN (MRE11-RAD51-NBS1) associate with seDSBs, interacting with each other and BRCA1. The HR nucleases EXO1 and DNA2 are also recruited and colocalize with each other and with the repair helicase Bloom syndrome protein (BLM), demonstrating multiple simultaneous resection events. Quantification of replication protein A (RPA) accumulation and ssDNA generation shows that resection is completed 2 to 4 h after break induction. However, both BRCA1 and BLM persist later into HR, demonstrating potential roles in homology search and repair resolution. Furthermore, we show that initial recruitment of BRCA1 and removal of Ku are largely independent of MRE11 exonuclease activity but dependent on MRE11 endonuclease activity. Combined, our observations provide a detailed description of resection during HR repair.
Keywords: BRCA1; DNA damage; DNA repair; homologous recombination; resection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of BRCA1-BARD1 function in DNA end resection and DNA protection.Nature. 2024 Oct;634(8033):492-500. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07909-9. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39261728 Free PMC article.
-
Release of Ku and MRN from DNA ends by Mre11 nuclease activity and Ctp1 is required for homologous recombination repair of double-strand breaks.PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002271. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21931565 Free PMC article.
-
CtIP promotes the motor activity of DNA2 to accelerate long-range DNA end resection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Apr 21;117(16):8859-8869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2001165117. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32241893 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of repair pathway choice at two-ended DNA double-strand breaks.Mutat Res. 2017 Oct;803-805:51-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.07.011. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Mutat Res. 2017. PMID: 28781144 Review.
-
DNA End Resection: Facts and Mechanisms.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun;14(3):126-130. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 May 27. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27240470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The MRN complex and topoisomerase IIIa-RMI1/2 synchronize DNA resection motor proteins.J Biol Chem. 2023 Feb;299(2):102802. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102802. Epub 2022 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36529288 Free PMC article.
-
Topological Analysis of γH2AX and MRE11 Clusters Detected by Localization Microscopy during X-ray-Induced DNA Double-Strand Break Repair.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;13(21):5561. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215561. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771723 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC4 influences the DNA damage response and counteracts senescence by assembling with HDAC1/HDAC2 to control H2BK120 acetylation and homology-directed repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 12;52(14):8218-8240. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae501. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38874468 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils and micronuclei: An emerging link between genomic instability and cancer-driven inflammation.Mutat Res. 2022 Jan-Jun;824:111778. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2022.111778. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Mutat Res. 2022. PMID: 35334355 Free PMC article.
-
3D Single Molecule Super-Resolution Microscopy of Whole Nuclear Lamina.Front Chem. 2022 Apr 28;10:863610. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.863610. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35572104 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

