The role of discoidin domain receptor 2 in the renal dysfunction of alport syndrome mouse model
- PMID: 33706638
- PMCID: PMC7971217
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1896548
The role of discoidin domain receptor 2 in the renal dysfunction of alport syndrome mouse model
Abstract
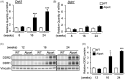
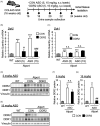
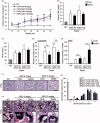
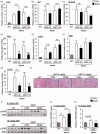
Alport syndrome (AS) is a hereditary glomerular nephritis caused by mutation in one of the type IV collagen genes α3/α4/α5 that encode the heterotrimer COL4A3/4/5. Failure to form a heterotrimer due to mutation leads to the dysfunction of the glomerular basement membrane, and end-stage renal disease. Previous reports have suggested the involvement of the receptor tyrosine kinase discoidin domain receptor (DDR) 1 in the progression of AS pathology. However, due to the similarity between DDR1 and DDR2, the role of DDR2 in AS pathology is unclear. Here, we investigated the involvement of DDR2 in AS using the X-linked AS mouse model. Mice were treated subcutaneously with saline or antisense oligonucleotide (ASO; 5 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg per week) for 8 weeks. Renal function parameters and renal histology were analyzed, and the gene expressions of inflammatory cytokines were determined in renal tissues. The expression level of DDR2 was highly elevated in kidney tissues of AS mice. Knockdown of Ddr2 using Ddr2-specific ASO decreased the Ddr2 expression. However, the DDR2 ASO treatment did not improve the proteinuria or decrease the BUN level. DDR2 ASO also did not significantly ameliorate the renal injury, inflammation and fibrosis in AS mice. These results showed that Ddr2 knockdown by ASO had no notable effect on the progression of AS indicating that DDR2 may not be critically involved in AS pathology. This finding may provide useful information and further understanding of the role of DDRs in AS.
Keywords: Alport syndrome; Type IV collagen; discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2); fibrosis; inflammatory cytokines; proteinuria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Collagen receptors integrin alpha2beta1 and discoidin domain receptor 1 regulate maturation of the glomerular basement membrane and loss of integrin alpha2beta1 delays kidney fibrosis in COL4A3 knockout mice.Matrix Biol. 2014 Feb;34:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24480069
-
Loss of collagen-receptor DDR1 delays renal fibrosis in hereditary type IV collagen disease.Matrix Biol. 2010 Jun;29(5):346-56. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 Mar 20. Matrix Biol. 2010. PMID: 20307660
-
Discoidin domain receptor 1 activation links extracellular matrix to podocyte lipotoxicity in Alport syndrome.EBioMedicine. 2021 Jan;63:103162. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103162. Epub 2020 Dec 16. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 33340991 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into the role of Discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) in cancer progression: a new avenue of therapeutic intervention.Matrix Biol. 2024 Jan;125:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2023.12.003. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Matrix Biol. 2024. PMID: 38081526 Review.
-
Glomerular pathology in Alport syndrome: a molecular perspective.Pediatr Nephrol. 2012 Jun;27(6):885-90. doi: 10.1007/s00467-011-1868-z. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 21455721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic and pharmacological tools to study the role of discoidin domain receptors in kidney disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 28;13:1001122. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1001122. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Modifiers of Mendelian Monogenic Collagen IV Nephropathies in Humans and Mice.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 25;14(9):1686. doi: 10.3390/genes14091686. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Keap1-Nrf2 Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitor UBE-1099 Ameliorates Progressive Phenotype in Alport Syndrome Mouse Model.Kidney360. 2021 Dec 1;3(4):687-699. doi: 10.34067/KID.0004572021. eCollection 2022 Apr 28. Kidney360. 2021. PMID: 35721612 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis, Diagnostic Challenges and Therapeutic Approaches of Alport Syndrome: A Primer for Clinicians.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 14;22(20):11063. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011063. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Journey of DDR1 and DDR2 Kinase Inhibitors as Rising Stars in the Fight Against Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 18;22(12):6535. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126535. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34207360 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hudson BG, Tryggvason K, Sundaramoorthy M, et al. . Alport's syndrome, Goodpasture's syndrome, and type IV collagen. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(25):2543–2556. - PubMed
-
- Gross O, Licht C, Anders HJ, Study Group Members of the Gesellschaft für Pädiatrische Nephrologie, et al.. Early angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in Alport syndrome delays renal failure and improves life expectancy. Kidney Int. 2012;81(5):494–501. - PubMed
-
- Omachi K, Miyakita R, Fukuda R, et al. . Long-term treatment with EGFR inhibitor erlotinib attenuates renal inflammatory cytokines but not nephropathy in Alport syndrome mouse model. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017;21(6):952–960. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
