Structural Arrangement within a Peptide Fibril Derived from the Glaucoma-Associated Myocilin Olfactomedin Domain
- PMID: 33683890
- PMCID: PMC8771281
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c11460
Structural Arrangement within a Peptide Fibril Derived from the Glaucoma-Associated Myocilin Olfactomedin Domain
Abstract
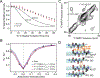
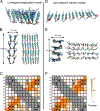
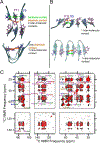
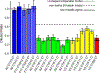
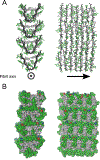
Myocilin-associated glaucoma is a new addition to the list of diseases linked to protein misfolding and amyloid formation. Single point variants of the ∼257-residue myocilin olfactomedin domain (mOLF) lead to mutant myocilin aggregation. Here, we analyze the 12-residue peptide P1 (GAVVYSGSLYFQ), corresponding to residues 326-337 of mOLF, previously shown to form amyloid fibrils in vitro and in silico. We applied solid-state NMR structural measurements to test the hypothesis that P1 fibrils adopt one of three predicted structures. Our data are consistent with a U-shaped fibril arrangement for P1, one that is related to the U-shape predicted previously in silico. Our data are also consistent with an antiparallel fibril arrangement, likely driven by terminal electrostatics. Our proposed structural model is reminiscent of fibrils formed by the Aβ(1-40) Iowa mutant peptide, but with a different arrangement of molecular turn regions. Taken together, our results strengthen the connection between mOLF fibrils and the broader amylome and contribute to our understanding of the fundamental molecular interactions governing fibril architecture and stability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The glaucoma-associated olfactomedin domain of myocilin forms polymorphic fibrils that are constrained by partial unfolding and peptide sequence.J Mol Biol. 2014 Feb 20;426(4):921-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 9. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24333014 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insights into Myocilin and Its Glaucoma-Causing Misfolded Olfactomedin Domain Variants.Acc Chem Res. 2021 May 4;54(9):2205-2215. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00060. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33847483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyloid fibril formation by the glaucoma-associated olfactomedin domain of myocilin.J Mol Biol. 2012 Aug 10;421(2-3):242-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.12.016. Epub 2011 Dec 13. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22197377 Free PMC article.
-
Stable calcium-free myocilin olfactomedin domain variants reveal challenges in differentiating between benign and glaucoma-causing mutations.J Biol Chem. 2019 Aug 23;294(34):12717-12728. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009419. Epub 2019 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31270212 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular structures of amyloid and prion fibrils: consensus versus controversy.Acc Chem Res. 2013 Jul 16;46(7):1487-96. doi: 10.1021/ar300282r. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Acc Chem Res. 2013. PMID: 23294335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myocilin misfolding and glaucoma: A 20-year update.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023 Jul;95:101188. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2023.101188. Epub 2023 May 20. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023. PMID: 37217093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiti F; Dobson CM, Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2006, 75, 333–366. - PubMed
-
- Iadanza MG; Jackson MP; Hewitt EW; Ranson NA; Radford SE, A new era for understanding amyloid structures and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2018, 19 (12), 755–773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

