Functional Expression of the Human Glucose Transporters GLUT2 and GLUT3 in Yeast Offers Novel Screening Systems for GLUT-Targeting Drugs
- PMID: 33681287
- PMCID: PMC7930720
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.598419
Functional Expression of the Human Glucose Transporters GLUT2 and GLUT3 in Yeast Offers Novel Screening Systems for GLUT-Targeting Drugs
Abstract
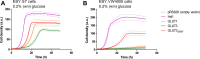
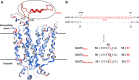
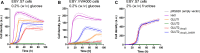
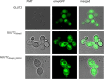
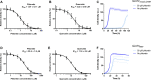
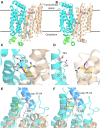
Human GLUT2 and GLUT3, members of the GLUT/SLC2 gene family, facilitate glucose transport in specific tissues. Their malfunction or misregulation is associated with serious diseases, including diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cancer. Despite being promising drug targets, GLUTs have only a few specific inhibitors. To identify and characterize potential GLUT2 and GLUT3 ligands, we developed a whole-cell system based on a yeast strain deficient in hexose uptake, whose growth defect on glucose can be rescued by the functional expression of human transporters. The simplicity of handling yeast cells makes this platform convenient for screening potential GLUT2 and GLUT3 inhibitors in a growth-based manner, amenable to high-throughput approaches. Moreover, our expression system is less laborious for detailed kinetic characterization of inhibitors than alternative methods such as the preparation of proteoliposomes or uptake assays in Xenopus oocytes. We show that functional expression of GLUT2 in yeast requires the deletion of the extended extracellular loop connecting transmembrane domains TM1 and TM2, which appears to negatively affect the trafficking of the transporter in the heterologous expression system. Furthermore, single amino acid substitutions at specific positions of the transporter sequence appear to positively affect the functionality of both GLUT2 and GLUT3 in yeast. We show that these variants are sensitive to known inhibitors phloretin and quercetin, demonstrating the potential of our expression systems to significantly accelerate the discovery of compounds that modulate the hexose transport activity of GLUT2 and GLUT3.
Keywords: GLUT2; GLUT3; Glucose transport inhibitor; drug screening system; hxt0 yeast strain.
Copyright © 2021 Schmidl, Tamayo Rojas, Iancu, Choe and Oreb.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of new GLUT2-selective inhibitors through in silico ligand screening and validation in eukaryotic expression systems.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 2;11(1):13751. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93063-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34215797 Free PMC article.
-
GLUT3 inhibitor discovery through in silico ligand screening and in vivo validation in eukaryotic expression systems.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 26;12(1):1429. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05383-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35082341 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis of liver-type (GLUT2) and brain-type (GLUT3) glucose transporters: expression of chimeric transporters in Xenopus oocytes suggests an important role for putative transmembrane helix 7 in determining substrate selectivity.Biochemistry. 1996 Dec 24;35(51):16519-27. doi: 10.1021/bi962210n. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8987985
-
Ligand Screening Systems for Human Glucose Transporters as Tools in Drug Discovery.Front Chem. 2018 May 25;6:183. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00183. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2018. PMID: 29888221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, function and regulation of mammalian glucose transporters of the SLC2 family.Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1155-1175. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02411-3. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Pflugers Arch. 2020. PMID: 32591905 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GLUT4 dispersal at the plasma membrane of adipocytes: a super-resolved journey.Biosci Rep. 2023 Oct 31;43(10):BSR20230946. doi: 10.1042/BSR20230946. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37791639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discrimination of GLUTs by Fructose Isomers Enables Simultaneous Screening of GLUT5 and GLUT2 Activity in Live Cells.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 May 19;18(5):1089-1100. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00682. Epub 2023 Apr 28. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37116192 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of new GLUT2-selective inhibitors through in silico ligand screening and validation in eukaryotic expression systems.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 2;11(1):13751. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93063-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34215797 Free PMC article.
-
The PTP1B Inhibitor Trodusquemine (MSI-1436) Improves Glucose Uptake in Equine Metabolic Syndrome Affected Liver through Anti-Inflammatory and Antifibrotic Activity.Int J Inflam. 2023 Sep 30;2023:3803056. doi: 10.1155/2023/3803056. eCollection 2023. Int J Inflam. 2023. PMID: 37808009 Free PMC article.
-
EFR3 and phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIα regulate insulin-stimulated glucose transport and GLUT4 dispersal in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Biosci Rep. 2022 Jul 29;42(7):BSR20221181. doi: 10.1042/BSR20221181. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35735144 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

