P2X7 Receptor Agonist 2'(3')-O-(4-Benzoylbenzoyl)ATP Differently Modulates Cell Viability and Corticostriatal Synaptic Transmission in Experimental Models of Huntington's Disease
- PMID: 33679392
- PMCID: PMC7933594
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.633861
P2X7 Receptor Agonist 2'(3')-O-(4-Benzoylbenzoyl)ATP Differently Modulates Cell Viability and Corticostriatal Synaptic Transmission in Experimental Models of Huntington's Disease
Abstract
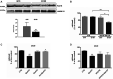
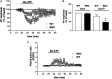
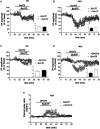
Huntington's disease (HD) is a life-threatening neurodegenerative disorder. Altered levels and functions of the purinergic ionotropic P2X7 receptors (P2X7Rs) have been found in animal and cellular models of HD, suggesting their possible role in the pathogenesis of the disease; accordingly, the therapeutic potential of P2X7R antagonists in HD has been proposed. Here we further investigated the effects of P2X7R ligands in in vitro and ex vivo HD experimental models. In ST14A/Q120 rat striatal cells, we found a reduction of P2X7R expression; however, the P2X7R agonist 2'(3')-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)adenosine-5'-triphosphate (BzATP) induced cellular death, and this effect was fully reversed by the antagonist periodate-oxidized adenosine 5'-triphosphate (OxATP). Moreover, in corticostriatal slices from symptomatic R6/2 mice, BzATP reduced the synaptic transmission to a larger extent than in wild-type (WT) mice. Such an effect was accompanied by a concomitant increase of the paired-pulse ratio, suggesting a presynaptic inhibitory action. This was confirmed to be the case, since while the effects of BzATP were unaffected by the P2X7R antagonist OxATP, they were blocked by the adenosine A1 receptor (A1R) antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX), suggesting possible BzATP hydrolysis to 2'(3')-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)adenosine (Bz-adenosine) and consequent activation of A1Rs as a mechanism. Taken together, these data point out that 1) P2X7R expression and activity are confirmed to be altered in the presence of HD mutation; 2) in some experimental settings, such an abnormal functioning can be ascribed to presynaptic A1Rs activation.
Keywords: BzATP; DPCPX; Huntington’s disease; OxATP; P2X7 receptor; adenosine; adenosine A1 receptor; corticostriatal slices.
Copyright © 2021 Martire, Pepponi, Liguori, Volonté and Popoli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Purinergic Signaling in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Huntington's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jul 1;15:657338. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.657338. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34276284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ecto-nucleotidases and nucleoside transporters mediate activation of adenosine receptors on hippocampal mossy fibers by P2X7 receptor agonist 2'-3'-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)-ATP.J Neurosci. 2004 Aug 11;24(32):7128-39. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2093-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15306646 Free PMC article.
-
Expression, pharmacology and functional activity of adenosine A1 receptors in genetic models of Huntington's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Nov;71:193-204. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.08.013. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 25132555
-
P2X7 purinoceptors contribute to the death of Schwann cells transplanted into the spinal cord.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Oct 3;4(10):e829. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.343. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24091672 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Adenosine Tone and Adenosine Receptors in Huntington's Disease.J Caffeine Adenosine Res. 2018 Jun 1;8(2):43-58. doi: 10.1089/caff.2018.0006. J Caffeine Adenosine Res. 2018. PMID: 30023989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pannexin-1 regulation of ATP release promotes the invasion of pituitary adenoma.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Feb;48(2):317-332. doi: 10.1007/s40618-024-02445-9. Epub 2024 Nov 11. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 39527372
-
Metabolic reprograming mediated by tumor cell-intrinsic type I IFN signaling is required for CD47-SIRPα blockade efficacy.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 9;15(1):5759. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50136-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38982116 Free PMC article.
-
Role and therapeutic targets of P2X7 receptors in neurodegenerative diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 2;15:1345625. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1345625. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38370420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic Signaling in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Huntington's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jul 1;15:657338. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.657338. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34276284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the P2 × 7 receptor in neurodegenerative diseases and its pharmacological properties.Cell Biosci. 2023 Dec 13;13(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01161-w. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38093352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G., Boeynaems J. M., Barnard E. A., Boyer J. L., Kennedy C., et al. (2006). International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 58 (3), 281–341. 10.1124/pr.58.3.3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

