The impact of FGF19/FGFR4 signaling inhibition in antitumor activity of multi-kinase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 33674622
- PMCID: PMC7935880
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84117-9
The impact of FGF19/FGFR4 signaling inhibition in antitumor activity of multi-kinase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
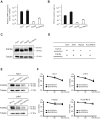
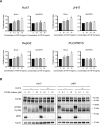
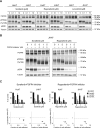
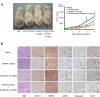
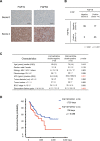
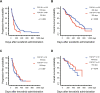
FGF19/FGFR4 autocrine signaling is one of the main targets for multi-kinase inhibitors (MKIs). However, the molecular mechanisms underlying FGF19/FGFR4 signaling in the antitumor effects to MKIs in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain unclear. In this study, the impact of FGFR4/ERK signaling inhibition on HCC following MKI treatment was analyzed in vitro and in vivo assays. Serum FGF19 in HCC patients treated using MKIs, such as sorafenib (n = 173) and lenvatinib (n = 40), was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Lenvatinib strongly inhibited the phosphorylation of FRS2 and ERK, the downstream signaling molecules of FGFR4, compared with sorafenib and regorafenib. Additional use of a selective FGFR4 inhibitor with sorafenib further suppressed FGFR4/ERK signaling and synergistically inhibited HCC cell growth in culture and xenograft subcutaneous tumors. Although serum FGF19high (n = 68) patients treated using sorafenib exhibited a significantly shorter progression-free survival and overall survival than FGF19low (n = 105) patients, there were no significant differences between FGF19high (n = 21) and FGF19low (n = 19) patients treated using lenvatinib. In conclusion, robust inhibition of FGF19/FGFR4 is of importance for the exertion of antitumor effects of MKIs. Serum FGF19 levels may function as a predictive marker for drug response and survival in HCC patients treated using sorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
Tatsuo Kanda received research support from Eisai. Naoya Kato received grant support, advisory fee, and honoraria from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Merck & Co., Inc. and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implications of FGF19 on sorafenib-mediated nitric oxide production in hepatocellular carcinoma cells - a short report.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Feb;41(1):85-91. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0354-4. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 28983785
-
Lenvatinib suppresses cancer stem-like cells in HCC by inhibiting FGFR1-3 signaling, but not FGFR4 signaling.Carcinogenesis. 2021 Feb 11;42(1):58-69. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgaa049. Carcinogenesis. 2021. PMID: 32449510
-
FGF19/FGFR4 signaling contributes to the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 9;36(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0478-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28069043 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted inhibition of the FGF19-FGFR4 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma; translational safety considerations.Liver Int. 2014 Jul;34(6):e1-9. doi: 10.1111/liv.12462. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 24393342 Review.
-
Effect of Lenvatinib on a Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 Expression: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Intern Med. 2021 Jun 1;60(11):1709-1715. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.6580-20. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33390501 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Potential Preclinical Drugs and their Future.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(1):2-14. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221216114350. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 36529919 Review.
-
Patient tissue-derived FGFR4-variant and wild-type colorectal cancer organoid development and anticancer drug sensitivity testing.Heliyon. 2024 May 14;10(10):e30985. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30985. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38826758 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis of Bile Acid-FXR-FGF15/19 Signaling Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 27;23(11):6046. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116046. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis identifies endocrine fibroblast growth factors as promising prognostic markers for colorectal carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 20;14(1):28754. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79341-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39567612 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs) and Noncanonical Partners in Cancer Signaling.Cells. 2021 May 14;10(5):1201. doi: 10.3390/cells10051201. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34068954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

