MicroRNAs: Their Role in Metastasis, Angiogenesis, and the Potential for Biomarker Utility in Bladder Carcinomas
- PMID: 33672684
- PMCID: PMC7924383
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13040891
MicroRNAs: Their Role in Metastasis, Angiogenesis, and the Potential for Biomarker Utility in Bladder Carcinomas
Abstract
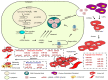
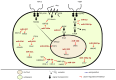
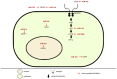
Angiogenesis is the process of generating new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels with a vital role in tumor growth and metastasis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are noncoding RNAs that exert post-transcriptional control of protein regulation. They participate in the development and progression of several cancers including bladder cancer (BLCA). In cancer tissue, changes in microRNA expression exhibit tissue specificity with high levels of stability and detectability. miRNAs are less vulnerable to degradation, making them novel targets for therapeutic approaches. A suitable means of targeting aberrant activated signal transduction pathways in carcinogenesis of BLCA is possibly through altering the expression of key miRNAs that regulate them, exerting a strong effect on signal transduction. Precaution must be taken, as the complexity of miRNA regulation might result in targeting several downstream tumor suppressors or oncogenes, enhancing the effect further. Since exosomes contain both mRNA and miRNA, they could therefore possibly be more effective in targeting a recipient cell if they deliver a specific miRNA to modify the recipient cell protein production and gene expression. In this review, we discuss the molecules that have been shown to play a significant role in BLCA tumor development. We also discuss the roles of various miRNAs in BLCA angiogenesis and metastasis. Advances in the management of metastatic BLCA have been limited; miRNA mimics and molecules targeted at miRNAs (anti-miRs) as well as exosomes could serve as therapeutic modalities or as diagnostic biomarkers.
Keywords: EMT; adhesion molecules; angiogenesis; bladder cancer; exosomes; metastasis; microRNA; urothelial bladder carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A step-by-step microRNA guide to cancer development and metastasis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017 Aug;40(4):303-339. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0341-9. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017. PMID: 28748501 Review.
-
Global analysis of miRNA-mRNA regulation pair in bladder cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Mar 3;20(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02538-w. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35241117 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-93-5p as an important driver of bladder cancer progression.Transl Androl Urol. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):286-299. doi: 10.21037/tau-22-872. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Transl Androl Urol. 2023. PMID: 36915886 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Exosomal Long Noncoding RNA TERC as a Noninvasive Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma.J Immunol Res. 2022 Jan 25;2022:9038808. doi: 10.1155/2022/9038808. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35127956 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting miRNAs and Other Non-Coding RNAs as a Therapeutic Approach: An Update.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Apr 13;9(2):27. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9020027. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37104009 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Downregulation of miR-135b-5p Suppresses Progression of Esophageal Cancer and Contributes to the Effect of Cisplatin.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 1;11:679348. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.679348. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34277424 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Angiogenesis in Bladder Cancer.Curr Oncol Rep. 2023 Jul;25(7):709-728. doi: 10.1007/s11912-023-01421-5. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Curr Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37052868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Precision Medicine for Head and Neck Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 4;16(21):3716. doi: 10.3390/cancers16213716. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of N6-Methylandenosine-Related Long Non-Coding RNAs Signature in Prognosis and Tumor Microenvironment of Bladder Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 24;12:774307. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.774307. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35141159 Free PMC article.
-
Vimentin Is at the Heart of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Mediated Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 5;13(19):4985. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194985. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

