Molecular Targeting of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR)
- PMID: 33670650
- PMCID: PMC7922143
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26041076
Molecular Targeting of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR)
Abstract
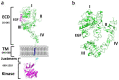
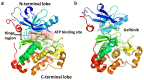
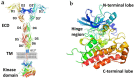
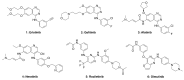
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) are two extensively studied membrane-bound receptor tyrosine kinase proteins that are frequently overexpressed in many cancers. As a result, these receptor families constitute attractive targets for imaging and therapeutic applications in the detection and treatment of cancer. This review explores the dynamic structure and structure-function relationships of these two growth factor receptors and their significance as it relates to theranostics of cancer, followed by some of the common inhibition modalities frequently employed to target EGFR and VEGFR, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), antibodies, nanobodies, and peptides. A summary of the recent advances in molecular imaging techniques, including positron emission tomography (PET), single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT), computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and optical imaging (OI), and in particular, near-IR fluorescence imaging using tetrapyrrolic-based fluorophores, concludes this review.
Keywords: EGFR; TKI; VEGFR; cancer; imaging; overexpression; peptide; protein; tyrosine kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidines as EGFR and VEGFR Kinase Inhibitors: A Comprehensive SAR Review.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(36):5918-5936. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230815115111. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37581522 Review.
-
Gallocin-derived Engineered Peptides Targeting EGFR and VEGFR in Colorectal Cancer: A Bioinformatic Approach.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(18):1599-1614. doi: 10.2174/0115680266295587240522050712. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38840394
-
Recent advances in small molecule inhibitors of VEGFR and EGFR signaling pathways.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(12):1571-90. doi: 10.2174/156802611795860924. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21510831 Review.
-
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor-based high-affinity PET radiopharmaceutical targets vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.J Nucl Med. 2014 Sep;55(9):1525-31. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.138925. Epub 2014 Jun 26. J Nucl Med. 2014. PMID: 24970912
-
From Tumor to Bone: Growth Factor Receptors as Key Players in Cancer Metastasis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 May 13;29(5):184. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2905184. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38812320 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Metabolic Profiling of Synechocystis sp. Extract Encapsulated in Nano-Liposomes and Nano-Niosomes Using LC-MS, Complemented by Molecular Docking Studies.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;13(8):581. doi: 10.3390/biology13080581. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194519 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of new 1,3-diphenylurea appended aryl pyridine derivatives as apoptosis inducers through c-MET and VEGFR-2 inhibition: design, synthesis, in vivo and in silico studies.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Jun 12;15(7):2553-2569. doi: 10.1039/d4md00280f. eCollection 2024 Jul 17. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39026631
-
Zero-Background Small-Molecule Sensors for Near-IR Fluorescent Imaging of Biomacromolecular Targets in Cells.ACS Sens. 2023 Mar 24;8(3):1109-1118. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.2c02342. Epub 2023 Mar 3. ACS Sens. 2023. PMID: 36866808 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Radiolabeling, and Biodistribution Study of a Novel DOTA-Peptide for Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptors in the Molecular Imaging of Breast Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 4;16(7):899. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070899. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065596 Free PMC article.
-
Solid Phase Synthesis, DFT Calculations, Molecular Docking, and Biological Studies of Symmetrical N 2,N 4,N 6-Trisubstituted-1,3,5-triazines.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 31;9(32):34428-34444. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c01980. eCollection 2024 Aug 13. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39157158 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

