Mayday sustains trans-synaptic BMP signaling required for synaptic maintenance with age
- PMID: 33667157
- PMCID: PMC7935490
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.54932
Mayday sustains trans-synaptic BMP signaling required for synaptic maintenance with age
Abstract
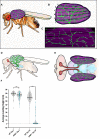
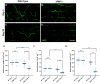
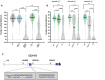
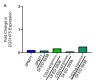
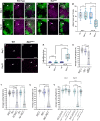
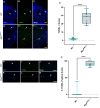
Maintaining synaptic structure and function over time is vital for overall nervous system function and survival. The processes that underly synaptic development are well understood. However, the mechanisms responsible for sustaining synapses throughout the lifespan of an organism are poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that a previously uncharacterized gene, CG31475, regulates synaptic maintenance in adult Drosophila NMJs. We named CG31475 mayday due to the progressive loss of flight ability and synapse architecture with age. Mayday is functionally homologous to the human protein Cab45, which sorts secretory cargo from the Trans Golgi Network (TGN). We find that Mayday is required to maintain trans-synaptic BMP signaling at adult NMJs in order to sustain proper synaptic structure and function. Finally, we show that mutations in mayday result in the loss of both presynaptic motor neurons as well as postsynaptic muscles, highlighting the importance of maintaining synaptic integrity for cell viability.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Drosophila; flight; genetics; genomics; neuromuscular junction; neuroscience; synapse.
© 2021, Sidisky et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JS, DW, SH, MO, RC, DB No competing interests declared
Figures

Similar articles
-
Importin-beta11 regulates synaptic phosphorylated mothers against decapentaplegic, and thereby influences synaptic development and function at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.J Neurosci. 2010 Apr 14;30(15):5253-68. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3739-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20392948 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroligin 4 regulates synaptic growth via the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 3;292(44):17991-18005. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.810242. Epub 2017 Sep 14. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28912273 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic glutamate receptors regulate local BMP signaling at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.Development. 2014 Jan;141(2):436-47. doi: 10.1242/dev.097758. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Development. 2014. PMID: 24353060 Free PMC article.
-
Synapse development and maturation at the drosophila neuromuscular junction.Neural Dev. 2020 Aug 2;15(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13064-020-00147-5. Neural Dev. 2020. PMID: 32741370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indirect flight muscles in Drosophila melanogaster as a tractable model to study muscle development and disease.Int J Dev Biol. 2020;64(1-2-3):167-173. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.190333un. Int J Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32659005 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved analysis method of neuromuscular junction in Drosophila larvae by transmission electron microscopy.Anat Sci Int. 2022 Jan;97(1):147-154. doi: 10.1007/s12565-021-00635-6. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Anat Sci Int. 2022. PMID: 34661863 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein signaling: the pathway and its regulation.Genetics. 2024 Feb 7;226(2):iyad200. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad200. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38124338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptic defects in a drosophila model of muscular dystrophy.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 May 15;18:1381112. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1381112. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38812789 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing dopaminergic neuron vulnerability using genome-wide analysis.Genetics. 2021 Aug 9;218(4):iyab081. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab081. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 34038543 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis reveals novel regulators of synaptic maintenance in Drosophila.Genetics. 2023 Apr 6;223(4):iyad025. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad025. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 36799927 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

