Serum Exosomal miRNA-1226 as Potential Biomarker of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33664577
- PMCID: PMC7924134
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S296816
Serum Exosomal miRNA-1226 as Potential Biomarker of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality and it is urgent to find biomarkers for early detection of PDAC. Exosomal miRNAs are useful biomarkers for cancer detection. The aims of this study were to investigate the potential role of serum exosomal miRNA in detection of PDAC and to analyze the correlation between the levels of exosome miRNA and the tumor biological behaviors.
Materials and methods: Thirteen serum samples were collected from five patients with PDACs, three healthy individuals (HIs) and five benign pancreatic lesions (BP) for a high throughput profiling analysis to identify an altered miRNA expression patterns in PDAC. Candidate exosomal miRNAs were filtered based on a second independent cohort that included 17 PDACs and 12 benign pancreatic lesions by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Four miRNAs were selected for miRNA validation as PDAC biomarkers in a subsequent set of samples. The association between candidate exosomal miRNA and tumor behavior (tumor invasion or metastases) was evaluated in 17 PDACs. In vitro studies were performed to evaluate the role of candidate exosomal miRNA on cell viability, apoptosis and cell migration in two PDAC cell lines.
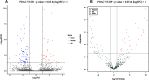
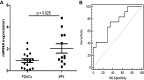
Results: The expression of 11 miRNAs showed same trend between PDAC and BP, and between PDAC and HIs. Six of them were upregulated (miR-203b-5p, miR-342-5p, miR-337-5p, miR-149-5p, miR-877-5p, miR-203a-3p), and five were downregulated (miR-1226-3p, miR-3182, miR-625-3p, miR-624-5p, miR-664a-5p). miR-1226-3p was selected as the candidate exosomal biomarker for the PDAC detection. The expression of serum exosomal miRNA-1226-3p was downregulated in PDACs compared to the BPs (p = 0.025). miR-1226-3p had acceptable performance in predicting [area under the curve (AUC) = 0.74] PDAC. Exosomal miRNA-1226-3p level in PDAC with invasion or metastases was lower than that without invasion or metastases (p = 0.028). Transfection of miRNA-1226-3p significantly inhibited the proliferation of PANC-1 and BXP-3 cells, stimulated cell apoptosis and inhibited cell migration.
Conclusion: Serum exosomal miRNA-1226-3p is a potential biomarker in diagnosing and predicting the tumor invasion or metastases of PDAC.
Keywords: exosome; miRNA; miRNA-1226-3p; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
© 2021 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Upregulated MicroRNA-483-3p is an Early Event in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and as a Powerful Liquid Biopsy Biomarker in PDAC.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Mar 25;14:2163-2175. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S288936. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33790579 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-296-5p Promotes Cell Invasion and Drug Resistance by Targeting Bcl2-Related Ovarian Killer, Leading to a Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer.Digestion. 2020;101(6):794-806. doi: 10.1159/000503225. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Digestion. 2020. PMID: 31563901
-
Exosomal miR-199a-3p Secreted From Cancer-Associated Adipocytes Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression.Cancer Med. 2024 Oct;13(20):e70265. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70265. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39431622 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Horizons in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer: The Role of Circulating microRNAs as Early Detection Biomarkers for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cureus. 2024 Jan 26;16(1):e53023. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53023. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38410292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Micro-RNAs Predict Response to Systemic Treatments in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients: Results from a Systematic Review of the Literature.Biomedicines. 2022 May 31;10(6):1287. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061287. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal RNAs: Novel Potential Biomarkers for Diseases-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 23;23(5):2461. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052461. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Exosome miR-203a-3p is a Potential Liquid Biopsy Marker for Assessing Tumor Progression in Breast Cancer Patients.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024 Sep 18;16:631-643. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S478328. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024. PMID: 39310782 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles and particles impact the systemic landscape of cancer.EMBO J. 2022 Sep 15;41(18):e109288. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021109288. Epub 2022 Sep 2. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 36052513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles: emerging biomarkers and therapies for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma diagnosis/prognosis and treatment.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Oct 14;20(1):446. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01641-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 36242076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic Cancer Small Extracellular Vesicles (Exosomes): A Tale of Short- and Long-Distance Communication.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;13(19):4844. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194844. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638330 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

