Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 33657295
- PMCID: PMC8436591
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2026982
Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus cabozantinib as compared with those of sunitinib in the treatment of previously untreated advanced renal-cell carcinoma are not known.
Methods: In this phase 3, randomized, open-label trial, we randomly assigned adults with previously untreated clear-cell, advanced renal-cell carcinoma to receive either nivolumab (240 mg every 2 weeks) plus cabozantinib (40 mg once daily) or sunitinib (50 mg once daily for 4 weeks of each 6-week cycle). The primary end point was progression-free survival, as determined by blinded independent central review. Secondary end points included overall survival, objective response as determined by independent review, and safety. Health-related quality of life was an exploratory end point.
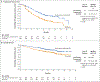
Results: Overall, 651 patients were assigned to receive nivolumab plus cabozantinib (323 patients) or sunitinib (328 patients). At a median follow-up of 18.1 months for overall survival, the median progression-free survival was 16.6 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 12.5 to 24.9) with nivolumab plus cabozantinib and 8.3 months (95% CI, 7.0 to 9.7) with sunitinib (hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.41 to 0.64; P<0.001). The probability of overall survival at 12 months was 85.7% (95% CI, 81.3 to 89.1) with nivolumab plus cabozantinib and 75.6% (95% CI, 70.5 to 80.0) with sunitinib (hazard ratio for death, 0.60; 98.89% CI, 0.40 to 0.89; P = 0.001). An objective response occurred in 55.7% of the patients receiving nivolumab plus cabozantinib and in 27.1% of those receiving sunitinib (P<0.001). Efficacy benefits with nivolumab plus cabozantinib were consistent across subgroups. Adverse events of any cause of grade 3 or higher occurred in 75.3% of the 320 patients receiving nivolumab plus cabozantinib and in 70.6% of the 320 patients receiving sunitinib. Overall, 19.7% of the patients in the combination group discontinued at least one of the trial drugs owing to adverse events, and 5.6% discontinued both. Patients reported better health-related quality of life with nivolumab plus cabozantinib than with sunitinib.
Conclusions: Nivolumab plus cabozantinib had significant benefits over sunitinib with respect to progression-free survival, overall survival, and likelihood of response in patients with previously untreated advanced renal-cell carcinoma. (Funded by Bristol Myers Squibb and others; CheckMate 9ER ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03141177.).
Copyright © 2021 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib Versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-cell Carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2021 Aug;80(2):256-257. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.04.039. Epub 2021 May 13. Eur Urol. 2021. PMID: 33992475 No abstract available.
-
Fortgeschrittenes Nierenzellkarzinom: Nivolumab/Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib.Aktuelle Urol. 2022 Feb;53(1):16-18. doi: 10.1055/a-1559-4893. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Aktuelle Urol. 2022. PMID: 35078256 German. No abstract available.
-
Cost Effectiveness of Treatment Sequences in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma.Eur Urol Oncol. 2023 Jun;6(3):331-338. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2023.01.011. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Eur Urol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36797084
Similar articles
-
Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (CheckMate 9ER): long-term follow-up results from an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2022 Jul;23(7):888-898. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00290-X. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Lancet Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35688173 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Patient-reported outcomes with first-line nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated in CheckMate 9ER: an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2022 Feb;23(2):292-303. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00693-8. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Lancet Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35032437 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up of efficacy and safety results from a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):1370-1385. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30413-9. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31427204 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab: A Review in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma.Target Oncol. 2022 Mar;17(2):193-201. doi: 10.1007/s11523-022-00866-1. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Target Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35175500 Review.
-
Management of adverse events associated with cabozantinib plus nivolumab in renal cell carcinoma: A review.Cancer Treat Rev. 2022 Feb;103:102333. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102333. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Cancer Treat Rev. 2022. PMID: 35033866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Outcomes of first-line treatment and their association with pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: Insights from a tertiary care institute in Pakistan.Ecancermedicalscience. 2024 Sep 3;18:1753. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2024.1753. eCollection 2024. Ecancermedicalscience. 2024. PMID: 39430088 Free PMC article.
-
Registration trials in countries without access to US standards of care - pitfalls of interpretation.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021 Jul;18(7):395-396. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00506-z. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33833435 No abstract available.
-
Incidence risk of peripheral edema in cancer patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: A PRISMA guideline systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 9;101(36):e30151. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030151. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36086680 Free PMC article.
-
Lenvatinib with or Without Everolimus in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma After Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapies.Oncologist. 2021 Jun;26(6):476-482. doi: 10.1002/onco.13770. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Oncologist. 2021. PMID: 33792094 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-Clear-Cell Renal Cancer.Kidney Cancer. 2022 Aug 4;6(2):115-127. doi: 10.3233/KCA-210012. eCollection 2022. Kidney Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36212797 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
