FoxA2 and RNA Pol II mediate human islet amyloid polypeptide turnover in ER-stressed pancreatic β-cells
- PMID: 33650632
- PMCID: PMC8011634
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20200984
FoxA2 and RNA Pol II mediate human islet amyloid polypeptide turnover in ER-stressed pancreatic β-cells
Abstract
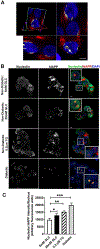
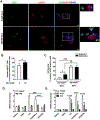
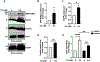
Here, we investigated transcriptional and trafficking mechanisms of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP) in normal and stressed β-cells. In high glucose-challenged human islets and rat insulinoma cells overexpressing hIAPP, cell fractionation studies revealed increased accumulation of hIAPP. Unexpectedly, a significant fraction (up to 22%) of hIAPP was found in the nuclear soluble and chromatin-enriched fractions of cultured human islet and rat insulinoma cells. The nucleolar accumulation of monomeric forms of hIAPP did not have any adverse effect on the proliferation of β-cells nor did it affect nucleolar organization or function. However, intact nucleolar organization and function were essential for hIAPP expression under normal and ER-stress conditions as RNA polymerase II inhibitor, α-amanitin, reduced hIAPP protein expression evoked by high glucose and thapsigargin. Promoter activity studies revealed the essential role of transcription factor FoxA2 in hIAPP promoter activation in ER-stressed β-cells. Transcriptome and secretory studies demonstrate that the biosynthetic and secretory capacity of islet β-cells was preserved during ER stress. Thus, the main reason for increased intracellular hIAPP accumulation is its enhanced biosynthesis under these adverse conditions.
Keywords: ER stress; FoxA2; islet amyloid polypeptide; nucleolus; trafficking; transcription.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests with the contents of this article.
Figures
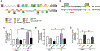
Similar articles
-
Functional proteasome complex is required for turnover of islet amyloid polypeptide in pancreatic β-cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 14;293(37):14210-14223. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002414. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30012886 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperones ameliorate beta cell dysfunction associated with human islet amyloid polypeptide overexpression.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 10;9(7):e101797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101797. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25010593 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrillation of human islet amyloid polypeptide and its toxicity to pancreatic β-cells under lipid environment.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020 Jan;1864(1):129422. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.129422. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020. PMID: 31491457
-
Human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP) - a curse in type II diabetes mellitus: insights from structure and toxicity studies.Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 4;402(2):133-153. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2020-0174. Print 2021 Jan 27. Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33544470 Review.
-
Molecular Structure, Membrane Interactions, and Toxicity of the Islet Amyloid Polypeptide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:5639875. doi: 10.1155/2016/5639875. Epub 2015 Nov 9. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 26636105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pomegranate peel, chokeberry leaves and Ironwort extract as novel natural inhibitors of amylin aggregation and cellular toxicity in pancreatic β cells.Biophys Chem. 2024 Jan;304:107130. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2023.107130. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Biophys Chem. 2024. PMID: 37952497 Free PMC article.
-
UTRs and Ago-2/miR-335 Complex Restricts Amylin Translation in Insulinoma and Human Pancreatic β-Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 5;25(17):9614. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179614. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273561 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Effect of Tyr-Ala Extracted from Zein on INS-1 Cells and Type 2 Diabetes High-Fat-Diet-Induced Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;11(6):1111. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061111. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740008 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Amylin Turnover, Misfolding and Toxicity in the Pancreas.Molecules. 2022 Feb 2;27(3):1021. doi: 10.3390/molecules27031021. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Insight into Vital Genes Responsible for β-cell Formation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1450:1-27. doi: 10.1007/5584_2023_778. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 37432546
References
-
- Hung MC, Link W. Protein localization in disease and therapy. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 20):3381–92. - PubMed
-
- Mulder H, Ahren B, Sundler F. Islet amyloid polypeptide and insulin gene expression are regulated in parallel by glucose in vivo in rats. Am J Physiol. 1996;271(6 Pt 1):E1008–14. - PubMed
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52(1):102–10. - PubMed
-
- Christmanson L, Rorsman F, Stenman G, Westermark P, Betsholtz C. The human islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) gene. Organization, chromosomal localization and functional identification of a promoter region. FEBS Lett. 1990;267(1):160–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

