LINC00649 promotes bladder cancer malignant progression by regulating the miR‑15a‑5p/HMGA1 axis
- PMID: 33649788
- PMCID: PMC7876990
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2021.7959
LINC00649 promotes bladder cancer malignant progression by regulating the miR‑15a‑5p/HMGA1 axis
Abstract
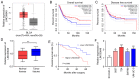
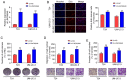
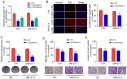
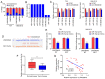
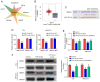
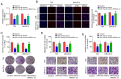
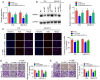
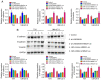
The aim of the present study was to explore the effects of LINC00649 on the proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer (BC) and identify possible mechanisms. Through TCGA database analysis of LINC00649 expression in bladder cancer and the association of LINC00649 with the BC patient prognosis, RT‑qPCR was employed for detecting LINC00649 expression in 60 clinical tissue specimens and cell lines of bladder cancer. The lentivirus stable transfection or small interfering RNA was used to increase or decrease the LINC00649 expression level in T24 and UM‑UC‑3 cells. CCK8 and clone formation assay were utilized to observe the effects of LINC00649 on the proliferation and colony formation of BC cells. Transwell experiment was performed to detect the effects of LINC00649 on the migration and invasion of bladder cancer. Bioinformatics database was used to identify the possible downstream targets of LINC00649 while RT‑qPCR, western blot analysis and dual luciferase reporter gene experiments were carried out to verify the possible molecular mechanism. The TCGA database analysis revealed a significantly high expression of LINC00649 in bladder cancer and an association of LINC00649 expression with overall survival rate of BC patients. As shown by RT‑qPCR detection, LINC00649 expression was notably upregulated in BC tissues and BC cell lines. In addition, statistical analyses unveiled that highly expressed LINC00649 was clearly associated with poor overall survival of bladder cancer. Based on the in vitro cell experiment, upregulated LINC00649 considerately enhanced the proliferation, migration and invasion of BC cells, as opposed to those in T24 and UM‑UC‑3 cells by suppressing LINC00649. Mechanically, LINC00649 may promote the malignant progression of bladder cancer by regulating miR‑15a‑5p to promote the HMGA1 expression axis. Overall, LINC00649 upregulates HMGA1 expression by binding to miR‑15a‑5p to enhance the proliferation, migration and invasion of BC cells. Thus, LINC00649 is a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for bladder cancer.
Keywords: bladder cancer; LINC00649; miR‑15a‑5p; HMGA1; malignant progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LINC00649 Facilitates the Cellular Process of Bladder Cancer Cells via Signaling Axis miR-16-5p/JARID2.Urol Int. 2022;106(3):304-312. doi: 10.1159/000506239. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Urol Int. 2022. PMID: 33789312
-
Exosomal LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating miR-15a-5p/HMGA2 axis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 May 21;53(6):673-682. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab041. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 33882126
-
Long noncoding RNA AC114812.8 promotes the progression of bladder cancer through miR-371b-5p/FUT4 axis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109605. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109605. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31706102
-
miRNAs role in bladder cancer pathogenesis and targeted therapy: Signaling pathways interplay - A review.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Feb;242:154316. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154316. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 36682282 Review.
-
Application of synthetic biology in bladder cancer.Chin Med J (Engl). 2022 Sep 20;135(18):2178-2187. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002344. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022. PMID: 36209735 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Diagnostic and Therapeutic Role of snoRNA and lincRNA in Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 4;15(4):1007. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041007. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HMGA1 is a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlated with Glycolysis in Lung Adenocarcinoma.J Cancer. 2024 Mar 25;15(10):2913-2927. doi: 10.7150/jca.89056. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38706894 Free PMC article.
-
High Mobility Group A1 (HMGA1): Structure, Biological Function, and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jul 4;18(11):4414-4431. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.72952. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35864955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Non-Coding RNA Landscape of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 22;14(9):2098. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092098. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565228 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of differentially expressed genes and a ceRNA network to identify hub lncRNAs and potential drugs for multiple sclerosis.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Feb 15;14(2):772-787. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35273684 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

