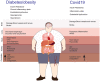
Diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance in COVID-19: molecular interrelationship and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 33648564
- PMCID: PMC7919999
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-021-00639-2
Diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance in COVID-19: molecular interrelationship and therapeutic implications
Abstract
Background: Our understanding of the pathophysiology of the COVID-19 manifestations and evolution has improved over the past 10 months, but the reasons why evolution is more severe in obese and diabetic patients are not yet completely understood.
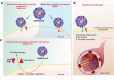
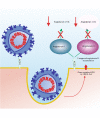
Main text: In the present review we discuss the different mechanisms that may contribute to explain the pathophysiology of COVID-19 including viral entrance, direct viral toxicity, endothelial dysfunction, thromboinflammation, dysregulation of the immune response, and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
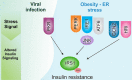
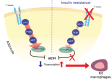
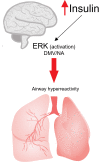
Conclusions: We show that the viral infection activates an integrated stress response, including activations of serine kinases such as PKR and PERK, which induce IRS-1 serine phosphorylation and insulin resistance. In parallel, we correlate and show the synergy of the insulin resistance of COVID-19 with this hormonal resistance of obesity and diabetes, which increase the severity of the disease. Finally, we discuss the potential beneficial effects of drugs used to treat insulin resistance and diabetes in patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Diabetes; ISR; Insulin resistance; Metformin; Obesity; iDPP4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures

Similar articles
-
Repurposing metformin for covid-19 complications in patients with type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021 Jun;43(3):265-270. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2021.1925294. Epub 2021 May 31. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021. PMID: 34057870 Review.
-
DPP-4 Inhibitors as Therapeutic Modulators of Immune Cell Function and Associated Cardiovascular and Renal Insulin Resistance in Obesity and Diabetes.Cardiorenal Med. 2013 Apr;3(1):48-56. doi: 10.1159/000348756. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Cardiorenal Med. 2013. PMID: 23946724 Free PMC article.
-
Maladaptive immune and inflammatory pathways lead to cardiovascular insulin resistance.Metabolism. 2013 Nov;62(11):1543-52. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23932846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase is a key modulator of insulin sensitivity in physiological conditions and in obesity in mice.Endocrinology. 2012 Nov;153(11):5261-74. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1400. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22948222
-
Plasma cell membrane glycoprotein 1 (PC-1): a marker of insulin resistance in obesity, uremia and diabetes mellitus.Clin Lab. 2004;50(5-6):271-8. Clin Lab. 2004. PMID: 15209435 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired glucose regulation, SARS-CoV-2 infections and adverse COVID-19 outcomes.Transl Res. 2022 Mar;241:52-69. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.11.002. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 34763125 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term diet and risk of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity.Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Dec 19;116(6):1672-1681. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac219. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35945354 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Immune Response in Patients with Insulin Resistance, Obesity, and Diabetes to COVID-19 Vaccination.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jul 5;11(7):1203. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11071203. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37515018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-diabetics and antimicrobials: Harmony of mutual interplay.World J Diabetes. 2021 Nov 15;12(11):1832-1855. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i11.1832. World J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34888011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Metabolic Risk Factors on COVID-19 Clinical Outcomes: An Extensive Review.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022;18(6):e090522204452. doi: 10.2174/1573403X18666220509154236. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35579126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cariou B, Hadjadj S, Wargny M, Pichelin M, Al-Salameh A, Allix I, Amadou C, Arnault G, Baudoux F, Bauduceau B, et al. Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study. Diabetologia. 2020;63(8):1500–15. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH, Nitsche A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181(2):271–80.e278. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

