A phase II study of first-line afatinib for patients aged ≥75 years with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer: North East Japan Study Group trial NEJ027
- PMID: 33648453
- PMCID: PMC7919080
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-07861-1
A phase II study of first-line afatinib for patients aged ≥75 years with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer: North East Japan Study Group trial NEJ027
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is most common among older individuals. However, polypharmacy and comorbidities, which are also more common in older individuals, can limit treatment options. Previous studies suggest that afatinib can be used safely and effectively in elderly patients. This study investigated the anti-tumour activity and safety profile of first-line afatinib in previously-untreated elderly Japanese patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: This was a single-arm, open-label, phase II study, performed in multiple centres in Japan. Previously untreated patients, aged ≥75 years, with EGFR mutation-positive (Del19 or L858R) advanced NSCLC were treated with afatinib 40 mg until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Adverse events (AEs) were managed with protocol-defined dose adjustments. The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR) by central review.
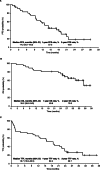
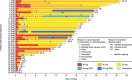
Results: In total, 38 patients received at least one dose of afatinib, and 37 were evaluable for response. Median age was 77.5 years (range 75-91), all patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1, and 60.5% had Del19-positive disease. Median follow-up was 838 days. ORR was 75.7% (2 complete responses and 26 partial responses). Median progression-free survival was 14.2 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 9.5-19.0). Median overall survival (OS) was 35.2 months (95% CI, 35.2-not reached); the 2-year OS rate was 78.3%. The most common grade 3/4 treatment-related AEs (TRAEs) were diarrhoea (28.9%), paronychia (23.7%), and rash/acne (15.8%). Dose reductions due to TRAEs were reported in 78.9% of patients, and eight (21.1%) patients discontinued afatinib due to TRAEs. No treatment-related deaths were reported.
Conclusion: Although dose adjustments were relatively common in this small group of Japanese patients aged ≥75 years with EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC, discontinuation occurred much less frequently, and most patients were able to stay on treatment for well over a year. Further, afatinib was associated with high response rates and prolonged PFS and OS.
Trial registration: The trial is registered with Japan Registry of Clinical Trials (JRCT) as trial number 031180136 (date of initial registration: 19 February 2019), and the University Hospital Network (UMIN) as trial number 000017877 (date of initial registration: 11 June 2015).
Keywords: Afatinib; Dose adjustment; EGFR mutation; Efficacy; Elderly patients; Japan; Non-small cell lung cancer; Safety.
Conflict of interest statement
O.Y. reports honoraria from Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., MSD, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and AstraZeneca. S.S. reports honoraria from Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., MSD, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer, Novartis, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd. S.W. reports honoraria from Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. M.M. reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly and Company, MSD, Novartis Pharma, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. O.H. reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis, and grants or funds from GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Bayer Health Care, Boehringer Ingelheim and Daiichi Sankyo. S.M. reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan, MSD, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and research funding to their institution from Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd. K.K. reports honoraria (speech fees) from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Eli Lilly and Company, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. A.G. reports honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim. Y.M., S.K., K.U., and T.N. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A phase II study of low starting dose of afatinib as first-line treatment in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (KTORG1402).Lung Cancer. 2019 Sep;135:175-180. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.03.030. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31446992 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical analysis of EGFR-positive non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line afatinib: A Nagano Lung Cancer Research Group.Thorac Cancer. 2019 May;10(5):1078-1085. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13047. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31006178 Free PMC article.
-
A phase II trial of erlotinib monotherapy for pretreated elderly patients with advanced EGFR wild-type non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Jun 5;8:220. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1214-9. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 26043909 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 25;(5):CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 18;3:CD010383. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010383.pub3 PMID: 27223332 Updated. Review.
-
Afatinib for the treatment of EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC: A review of clinical findings.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020 Sep;26(6):1461-1474. doi: 10.1177/1078155220931926. Epub 2020 Jun 20. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020. PMID: 32567494 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of erlotinib and its effects on the quality of life of older patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective, multicenter, dose-modification study.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2021 Oct;21(10):881-886. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14243. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2021. PMID: 34378299 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The difference between dacomitinib and afatinib in effectiveness and safety in first-line treatment of patients with advanced EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a real-world observational study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 19;24(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11956-w. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38373960 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Therapy for Older Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Guidelines from the French Society of Geriatric Oncology (SoFOG) and the French-Language Society of Pulmonology (SPLF)/French-Language Oncology Group (GOLF).Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 2;14(3):769. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030769. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35159036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with prolonged progression-free survival of patients treated with first-line afatinib for advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2024 Mar;15(7):529-537. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15212. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Thorac Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38279515 Free PMC article.
-
A Phase II Trial on Osimertinib as a First-Line Treatment for EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced NSCLC in Elderly Patients: The SPIRAL-0 Study.Oncologist. 2022 Nov 3;27(11):903-e834. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyac193. Oncologist. 2022. PMID: 36181763 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wu YL, Planchard D, Lu S, Sun H, Yamamoto N, Kim DW, et al. Pan-Asian adapted clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a CSCO-ESMO initiative endorsed by JSMO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(2):171–210. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy554. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, epidemiology and end results (SEER) stat fact sheets: lung and bronchus cancer. Available at: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html (Accessed 30 October 2020).
-
- Wu YL, Sequist LV, Tan EH, Geater SL, Orlov S, Zhang L, et al. Afatinib as first-line treatment of older patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: subgroup analyses of the LUX-Lung 3, LUX-Lung 6, and LUX-Lung 7 trials. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(4):e465–ee79. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2018.03.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

