A clear pathway to tubulointerstitial disease: is an exclusive focus on fibrosis justified?
- PMID: 33645547
- PMCID: PMC7919712
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI144803
A clear pathway to tubulointerstitial disease: is an exclusive focus on fibrosis justified?
Abstract
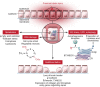
Tubulointerstitial accumulation of matrix proteins in human kidney biopsies is the best predictor of renal survival. In this issue of the JCI, Yen-Ting Chen et al. elegantly show that an endoplasmic reticulum resident protein, thioredoxin domain containing 5 (TXNDC5), is a key mediator of experimental kidney fibrosis. The researchers used knockout or conditional knockout animals to reduce Txndc5 expression, which reduced the accumulation of fibrous tissue in three models of chronic kidney disease (CKD), including unilateral ureteral obstruction, unilateral ischemia reperfusion injury, and folic acid nephropathy. More importantly, the studies demonstrate that the activated fibroblasts are almost exclusively responsible for producing matrix proteins. The study also showed that reducing Txndc5 in mice after tubulointerstitial fibrosis (TIF) was established mitigated the fibrosis. These experiments have obvious clinical importance but warrant caution because a key question remains unanswered. The impact of reducing TXNDC5 on renal function itself, the very heart of CKD, demands further exploration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
Endoplasmic reticulum protein TXNDC5 promotes renal fibrosis by enforcing TGF-β signaling in kidney fibroblasts.J Clin Invest. 2021 Mar 1;131(5):e143645. doi: 10.1172/JCI143645. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33465051 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
NLRP3 Deficiency Attenuates Renal Fibrosis and Ameliorates Mitochondrial Dysfunction in a Mouse Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model of Chronic Kidney Disease.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:8316560. doi: 10.1155/2017/8316560. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28348462 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum protein TXNDC5 promotes renal fibrosis by enforcing TGF-β signaling in kidney fibroblasts.J Clin Invest. 2021 Mar 1;131(5):e143645. doi: 10.1172/JCI143645. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33465051 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Fibrosis, Immune Cell Infiltration and Changes of TRPC Channel Expression after Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Trpc6-/- Mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(6):1484-1502. doi: 10.33594/000000103. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31099508
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress in the promotion of fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction.Biofactors. 2020 Sep;46(5):716-733. doi: 10.1002/biof.1673. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Biofactors. 2020. PMID: 32905648 Review.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for tubulointerstitial fibrosis.J Physiol. 2023 Jul;601(14):2801-2826. doi: 10.1113/JP284289. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37227074 Review.
Cited by
-
Deficiency of the Planar Cell Polarity Protein Intu Delays Kidney Repair and Suppresses Renal Fibrosis after Acute Kidney Injury.Am J Pathol. 2023 Mar;193(3):275-285. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2022.12.006. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Am J Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36586478 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

