Comparison of E. coli based self-inducible expression systems containing different human heat shock proteins
- PMID: 33633341
- PMCID: PMC7907268
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84188-8
Comparison of E. coli based self-inducible expression systems containing different human heat shock proteins
Abstract
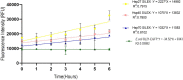
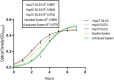
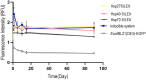
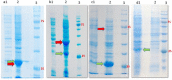
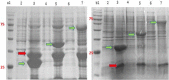
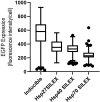
IPTG-inducible promoter is popularly used for the expression of recombinant proteins. However, it is not suitable at the industrial scale due to the high cost and toxicity on the producing cells. Recently, a Self-Inducible Expression (SILEX) system has developed to bypass such problems using Hsp70 as an autoinducer. Herein, the effect of other heat shock proteins on the autoinduction of green fluorescent protein (EGFP), romiplostim, and interleukin-2 was investigated. For quantitative measurements, EGFP expression was monitored after double-transformation of pET28a-EGFP and pET21a-(Hsp27/Hsp40/Hsp70) plasmids into E. coli using fluorimetry. Moreover, the expression level, bacterial growth curve, and plasmid and expression stability were compared to an IPTG- inducible system using EGFP. Statistical analysis revealed a significant difference in EGFP expression between autoinducible and IPTG-inducible systems. The expression level was higher in Hsp27 system than Hsp70/Hsp40 systems. However, the highest amount of expression was observed for the inducible system. IPTG-inducible and Hsp70 systems showed more lag-time in the bacterial growth curve than Hsp27/Hsp40 systems. A relatively stable EGFP expression was observed in SILEX systems after several freeze-thaw cycles within 90 days, while, IPTG-inducible system showed a decreasing trend compared to the newly transformed bacteria. Moreover, the inducible system showed more variation in the EGFP expression among different clones than clones obtained by SILEX systems. All designed SILEX systems successfully self-induced the expression of protein models. In conclusion, Hsp27 system could be considered as a suitable autoinducible system for protein expression due to less metabolic burden, lower variation in the expression level, suitable plasmid and expression stability, and a higher expression level.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid screening of high expressing Escherichia coli colonies using a novel dicistronic-autoinducible system.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Dec 11;20(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01711-2. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 34895227 Free PMC article.
-
Development of inducer-free expression plasmids based on IPTG-inducible promoters for Bacillus subtilis.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Jul 25;16(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0747-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 28743271 Free PMC article.
-
A self-inducible heterologous protein expression system in Escherichia coli.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 9;6:33037. doi: 10.1038/srep33037. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27611846 Free PMC article.
-
Design of inducible expression vectors for improved protein production in Ralstonia eutropha H16 derived host strains.J Biotechnol. 2016 Oct 10;235:92-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.04.026. Epub 2016 Apr 13. J Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27085887 Review.
-
Alternative regulation principles for the production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1996 Aug;46(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s002530050775. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1996. PMID: 8987528 Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for efficient production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli: alleviating the host burden and enhancing protein activity.Microb Cell Fact. 2022 Sep 15;21(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01917-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2022. PMID: 36109777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of Ni2+-functionalized polydopamine magnetic beads for facilitated purification of histidine-tagged proteins.AMB Express. 2023 Oct 13;13(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01613-z. AMB Express. 2023. PMID: 37833506 Free PMC article.
-
Design and characterization of a novel lytic protein against Clostridium difficile.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(12):4511-4521. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12010-0. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35699735 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Expression System on Recombinant Protein Production in Escherichia coli BL21.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 21;12:682001. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.682001. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34234760 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized production of a truncated form of the recombinant neuraminidase of influenza virus in Escherichia coli as host with suitable functional activity.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Nov 25;23(1):318. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02587-8. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39582000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riggs PD. Overview of protein expression vectors for E. coli. Curr. Protoc. Essential Lab. Tech. 2018;17:e23. doi: 10.1002/cpet.23. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

