A comparison of sunitinib with cabozantinib, crizotinib, and savolitinib for treatment of advanced papillary renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial
- PMID: 33592176
- PMCID: PMC8687736
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00152-5
A comparison of sunitinib with cabozantinib, crizotinib, and savolitinib for treatment of advanced papillary renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial
Abstract
Background: MET (also known as hepatocyte growth factor receptor) signalling is a key driver of papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC). Given that no optimal therapy for metastatic PRCC exists, we aimed to compare an existing standard of care, sunitinib, with the MET kinase inhibitors cabozantinib, crizotinib, and savolitinib for treatment of patients with PRCC.
Methods: We did a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial done in 65 centres in the USA and Canada. Eligible patients were aged 18 years or older with metastatic PRCC who had received up to one previous therapy (excluding vascular endothelial growth factor-directed and MET-directed agents). Patients were randomly assigned to receive sunitinib, cabozantinib, crizotinib, or savolitinib, with stratification by receipt of previous therapy and PRCC subtype. All drug doses were administered orally: sunitinib 50 mg, 4 weeks on and 2 weeks off (dose reductions to 37·5 mg and 25 mg allowed); cabozantinib 60 mg daily (reductions to 40 mg and 20 mg allowed); crizotinib 250 mg twice daily (reductions to 200 mg twice daily and 250 mg once daily allowed); and savolitinib 600 mg daily (reductions to 400 mg and 200 mg allowed). Progression-free survival (PFS) was the primary endpoint. Analyses were done in an intention-to-treat population, with patients who did not receive protocol therapy excluded from safety analyses. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02761057.
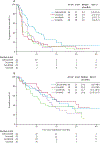
Findings: Between April 5, 2016, and Dec 15, 2019, 152 patients were randomly assigned to one of four study groups. Five patients were identified as ineligible post-randomisation and were excluded from these analyses, resulting in 147 eligible patients. Assignment to the savolitinib (29 patients) and crizotinib (28 patients) groups was halted after a prespecified futility analysis; planned accrual was completed for both sunitinib (46 patients) and cabozantinib (44 patients) groups. PFS was longer in patients in the cabozantinib group (median 9·0 months, 95% CI 6-12) than in the sunitinib group (5·6 months, 3-7; hazard ratio for progression or death 0·60, 0·37-0·97, one-sided p=0·019). Response rate for cabozantinib was 23% versus 4% for sunitinib (two-sided p=0·010). Savolitinib and crizotinib did not improve PFS compared with sunitinib. Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 31 (69%) of 45 patients receiving sunitinib, 32 (74%) of 43 receiving cabozantinib, ten (37%) of 27 receiving crizotinib, and 11 (39%) of 28 receiving savolitinib; one grade 5 thromboembolic event was recorded in the cabozantinib group.
Interpretation: Cabozantinib treatment resulted in significantly longer PFS compared with sunitinib in patients with metastatic PRCC.
Funding: National Institutes of Health and National Cancer Institute.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cabozantinib: a new first-line option for papillary renal cell carcinoma?Lancet. 2021 Feb 20;397(10275):645-647. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00316-0. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Lancet. 2021. PMID: 33592177 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Final Overall Survival Analysis of S1500: A Randomized, Phase II Study Comparing Sunitinib With Cabozantinib, Crizotinib, and Savolitinib in Advanced Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Clin Oncol. 2024 Nov 20;42(33):3911-3916. doi: 10.1200/JCO.24.00767. Epub 2024 Sep 10. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39255440 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Belzutifan plus cabozantinib as first-line treatment for patients with advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (LITESPARK-003): an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2025 Jan;26(1):64-73. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(24)00649-1. Lancet Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39756444 Clinical Trial.
-
Nilotinib versus imatinib for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed chronic phase, Philadelphia chromosome-positive, chronic myeloid leukaemia: 24-month minimum follow-up of the phase 3 randomised ENESTnd trial.Lancet Oncol. 2011 Sep;12(9):841-51. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70201-7. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Lancet Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21856226 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral budesonide for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 26;2015(10):CD007698. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007698.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic outcome of combination therapy using immune-checkpoint inhibitors and tyrosine kinase inhibitors for metastatic non-clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.Can Urol Assoc J. 2024 May;18(5):E162-E166. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.8548. Can Urol Assoc J. 2024. PMID: 38319607 Free PMC article.
-
A real-world pharmacovigilance study of FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) events for sunitinib.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 24;15:1407709. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1407709. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39114350 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Efficacy, Safety, and Subgroup Analysis of Savolitinib in Chinese Patients With NSCLCs Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Alterations.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2022 Sep 9;3(10):100407. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2022.100407. eCollection 2022 Oct. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2022. PMID: 36217329 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM63 is a sensitive and specific biomarker for MiT family aberration-associated renal cell carcinoma.Mod Pathol. 2021 Aug;34(8):1596-1607. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00803-z. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Mod Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33854184 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Surgery in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma in 2024.Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2024 Sep 5;18:11795549241272447. doi: 10.1177/11795549241272447. eCollection 2024. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39247714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang T, Gong J, Maia MC, Pal SK. Systemic Therapy for Non-Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2017; 37: 337–42. - PubMed
-
- Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE, Ulbright TM. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs—Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. European Urology 2016; 70: 93–105. - PubMed
-
- Pal SK, Ali SM, Yakirevich E, et al. Characterization of Clinical Cases of Advanced Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma via Comprehensive Genomic Profiling. Eur Urol 2018; 73: 71–8. - PubMed
-
- Albiges L, Guegan J, Le Formal A, et al. MET is a potential target across all papillary renal cell carcinomas: result from a large molecular study of pRCC with CGH array and matching gene expression array. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: 3411–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA180868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA093373/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA180863/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- CA180819/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- CA180868/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA180888/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180863/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180819/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA180820/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- CA180821/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous