Effects of pH on an IDP conformational ensemble explored by molecular dynamics simulation
- PMID: 33581430
- PMCID: PMC8024028
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106552
Effects of pH on an IDP conformational ensemble explored by molecular dynamics simulation
Abstract
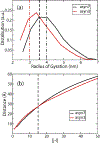
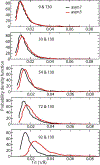
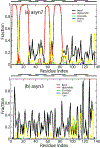
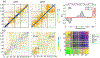
The conformational ensemble of intrinsically disordered proteins, such as α-synuclein, are responsible for their function and malfunction. Misfolding of α-synuclein can lead to neurodegenerative diseases, and the ability to study their conformations and those of other intrinsically disordered proteins under varying physiological conditions can be crucial to understanding and preventing pathologies. In contrast to well-folded peptides, a consensus feature of IDPs is their low hydropathy and high charge, which makes their conformations sensitive to pH perturbation. We examine a prominent member of this subset of IDPs, α-synuclein, using a divide-and-conquer scheme that provides enhanced sampling of IDP structural ensembles. We constructed conformational ensembles of α-synuclein under neutral (pH ~ 7) and low (pH ~ 3) pH conditions and compared our results with available information obtained from smFRET, SAXS, and NMR studies. Specifically, α-synuclein has been found to in a more compact state at low pH conditions and the structural changes observed are consistent with those from experiments. We also characterize the conformational and dynamic differences between these ensembles and discussed the implication on promoting pathogenic fibril formation. We find that under low pH conditions, neutralization of negatively charged residues leads to compaction of the C-terminal portion of α-synuclein while internal reorganization allows α-synuclein to maintain its overall end-to-end distance. We also observe different levels of intra-protein interaction between three regions of α-synuclein at varying pH and a shift towards more hydrophilic interactions with decreasing pH.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; FRET; Intrinsically disordered protein; Molecular dynamics.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
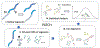

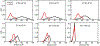
Similar articles
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Combined with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and/or Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Data for Characterizing Intrinsically Disordered Protein Conformational Ensembles.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 May 28;59(5):1743-1758. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00928. Epub 2019 Mar 18. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 30840442 Review.
-
Structural reorganization of alpha-synuclein at low pH observed by NMR and REMD simulations.J Mol Biol. 2009 Aug 28;391(4):784-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.06.063. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19576220 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational Ensembles of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein Consistent with NMR, SAXS, and Single-Molecule FRET.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Sep 16;142(37):15697-15710. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c02088. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32840111 Free PMC article.
-
A Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Approach to the Study of the Intrinsically Disordered Protein α-Synuclein.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Apr 22;59(4):1458-1471. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00921. Epub 2019 Apr 12. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 30933517
-
Recent Advances in Computational Protocols Addressing Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Biomolecules. 2019 Apr 11;9(4):146. doi: 10.3390/biom9040146. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30979035 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Electric Field on α-Synuclein Fibrils: Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 28;24(7):6312. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076312. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047286 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the Conformational Stability of the cl-Par-4 Tumor Suppressor via Site-Directed Mutagenesis.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 12;13(4):667. doi: 10.3390/biom13040667. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189414 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Conformational Space of the RNA Polymerase II C-Terminal Domain upon Phosphorylation.J Phys Chem B. 2023 Nov 2;127(43):9223-9235. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c02655. Epub 2023 Oct 23. J Phys Chem B. 2023. PMID: 37870995 Free PMC article.
-
A modular approach to map out the conformational landscapes of unbound intrinsically disordered proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jun 7;119(23):e2113572119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113572119. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35658083 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational Dynamics of Glucagon-like Peptide-2 with Different Electric Field.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 3;14(13):2722. doi: 10.3390/polym14132722. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dill KA and MacCallum JL, The Protein-Folding Problem, 50 Years On. Science, 2012. 338(6110): p. 1042–1046. - PubMed
-
- Tompa P, Intrinsically unstructured proteins. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2002. 27(10): p. 527–533. - PubMed
-
- Uversky VN, Oldfield CJ, and Dunker AK, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins in Human Diseases: Introducing the D2 Concept. Annual Review of Biophysics, 2008. 37(1): p. 215–246. - PubMed
-
- Oldfield CJ and Dunker AK, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Intrinsically Disordered Protein Regions. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2014. 83(1): p. 553–584. - PubMed
-
- Dyson HJ and Wright PE, Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2005. 6(3): p. 197–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

